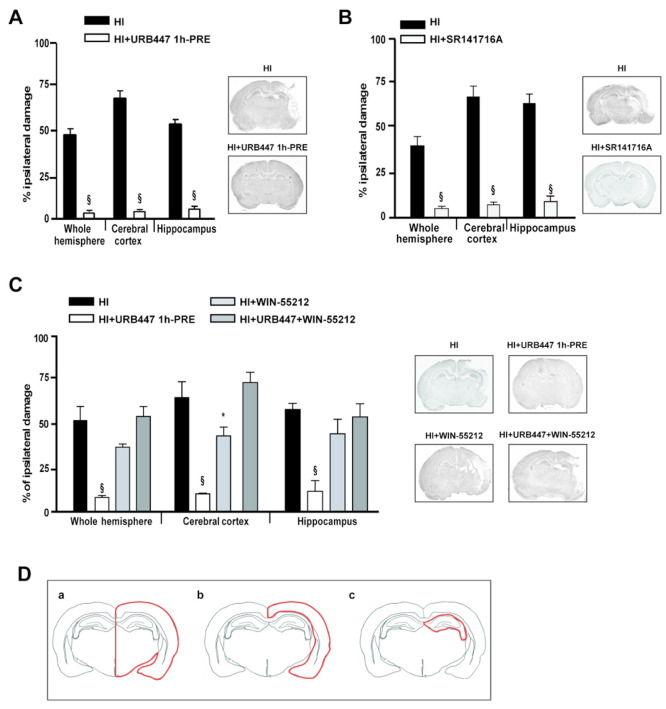
Figure 2.
Evaluation of brain damage after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia (HI) and treatment with URB447, SR141716A, and WIN-55,212-2. Infarct volume measured in the whole hemisphere, cerebral cortex, and hippocampus of 14-day-old rats subjected to HI on P7 and treated with (A) vehicle (HI) or URB447 1 mg/kg 1 h before HI (HI+URB447 1h-PRE); (B) vehicle (HI) or SR141716A 1 mg/kg 1 h before HI (HI+SR141716A); (C) vehicle (HI) or URB447 1 mg/kg 1 h before HI (HI+URB447), or WIN-55,212-2 1 mg/kg 1 h and 30 min before HI (HI+WIN-55,212-2), or URB447 plus WIN-55,212-2 (HI+URB447+WIN-55,212-2). Images represent coronal brain sections at the hippocampal level of each experimental group stained with toluidine blue. Results are expressed as percentage of ipsilateral damage calculated from bilateral regional volumes using the formula 100(L – R)/L, where L is the volume of the contralateral region and R is the volume of the ipsilateral region (N = 10/group). * P < 0.05, § P < 0.001, Mann–Whitney test and one-way ANOVA followed by Newman–Keuls multiple comparison test. (D) Representative drawing of the brain areas—whole hemisphere (a), cerebral cortex (b), and hippocampus (c)—analyzed in the histological experiments reported in panels A, B, and C.