Figure 3. Activation of EEC Trpa1 signaling facilitates enteric E. tarda clearance.
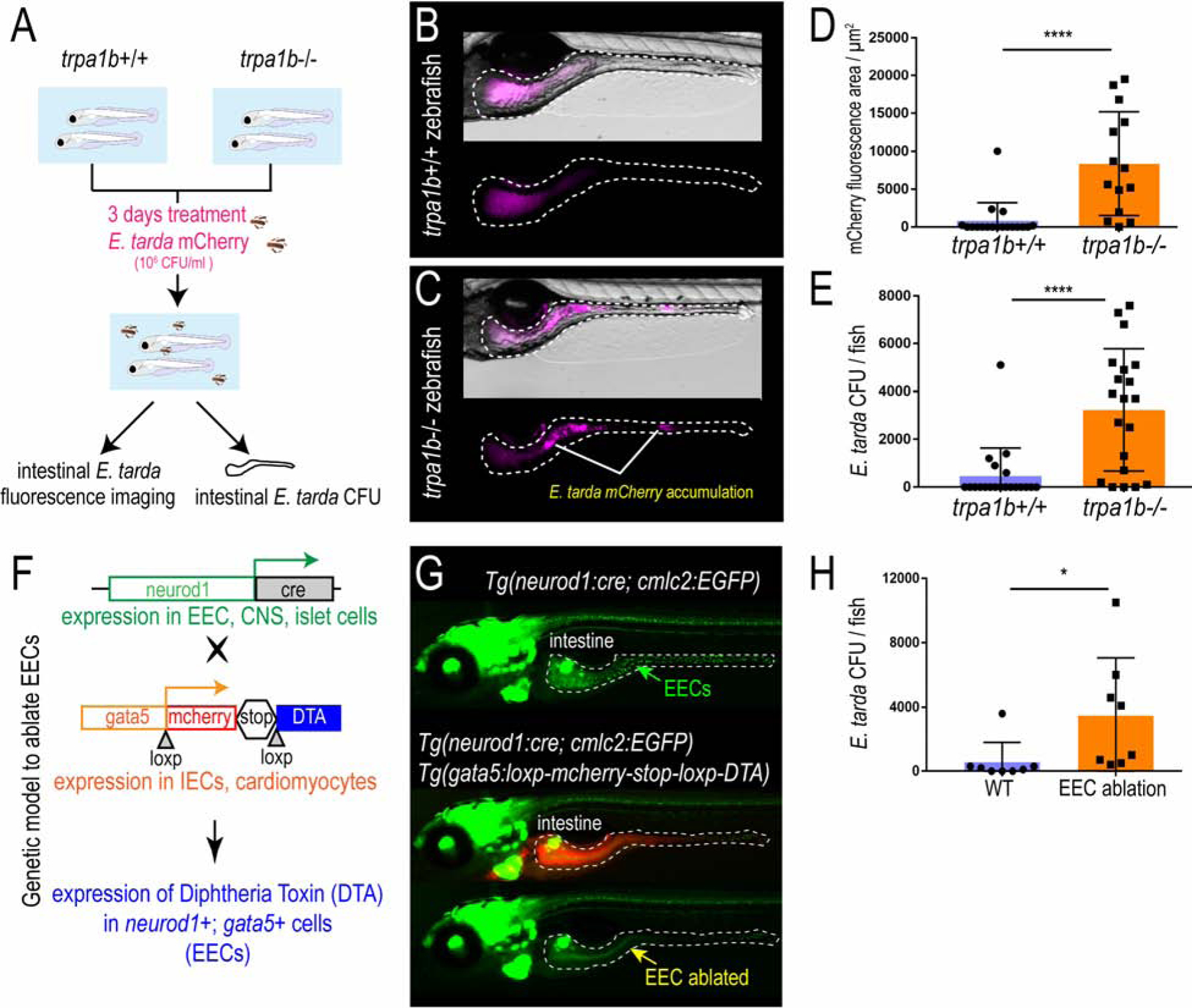
(A) Schematic of zebrafish E. tarda treatment. (B-C) Representative image of trpa1b+/+ or trpa1b−/− zebrafish treated with E. tarda expressing mCherry (E. tarda mCherry). (D) Quantification of E. tarda mCherry fluorescence in trpa1b+/+ or trpa1b−/− zebrafish intestine. (E) Quantification of intestinal E. tarda CFU in trpa1b+/+ or trpa1b−/− zebrafish. (F) Schematic of genetic model in which EECs are ablated via Cre-induced Diptheria Toxin (DTA) expression. (G) Representative image of Tg(neurod1:cre; cmlc2:EGFP) and Tg(neurod1:cre; cmlc2:EGFP); TgBAC(gata5:RSD) with EECs that are labelled by Tg(neurod1:EGFP). (H) Quantification of intestinal E. tarda CFU in WT or EEC ablated zebrafish. Student’s t-test was used in D, E, H. *p<0.05; ****p<0.0001.
