Fig. 5. Impaired synaptic plasticity in Ftsj1 KO brain.
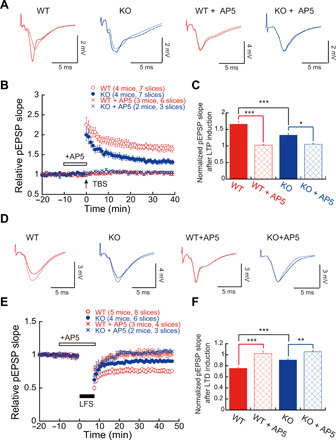
(A) Representative traces of pEPSPs recorded in CA1 region with and without N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist AP5 (50 μM). Traces with dashed lines represent basal pEPSPs, and traces with solid lines represent pEPSPs after TBS. (B) TBS-evoked LTP in hippocampal slices from WT and KO mice with and without 50 μM AP5. Seven slices from four WT mice and seven slices from four KO mice were used for LTP experiment. Six slices from three WT mice and three slices from two KO mice were used for LTP experiments in the presence of 50 μM AP5. (C) Impairment of NMDA receptor–dependent LTP in the KO mouse brain. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. Error bars present SEM. (D) Representative traces of pEPSPs recorded in CA1 region using LTD protocol. Traces with dashed lines represent basal pEPSPs, and traces with solid lines represent pEPSPs after LFS. (E) LFS-evoked LTD in hippocampal slices from WT and KO mice with and without 50 μM AP5. Eight slices from five WT mice and six slices from four KO mice were used for LTD experiment. Four slices from three WT mice and three slices from two KO mice were used for LTD experiments in the presence of 50 μM AP5. (F) NMDA receptor–dependent LTD was impaired in the KO mouse brain. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. Error bars present SEM.
