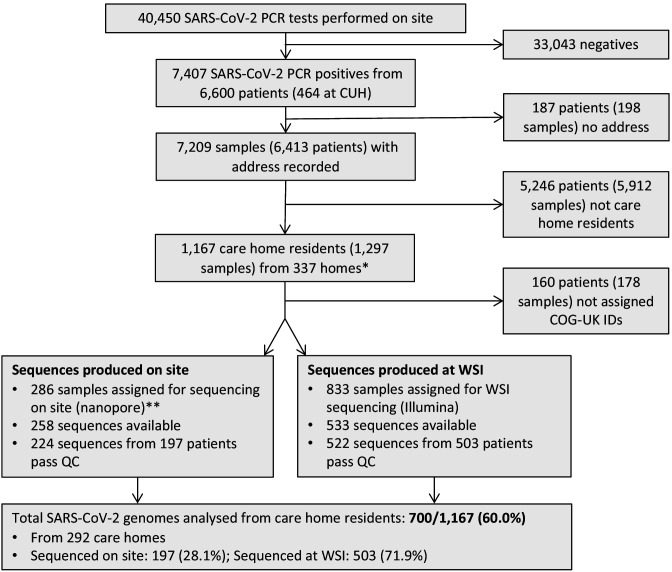
Figure 1. Study flow diagram Out of 6600 patients testing positive in the Cambridge Microbiology Public Health Laboratory (CMPHL) during the study period, 1167 were identified as being care home residents from 337 care homes.
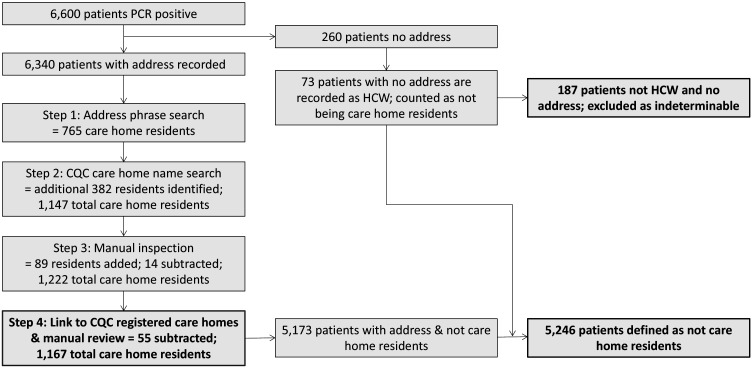
(The methodology for assigning care home status is described in main text and Figure 1—figure supplement 1). Out of 1297 samples from 1167 care home residents, 286 samples were assigned for nanopore sequencing on site and 833 samples for sequencing at the Wellcome Sanger Institute (WSI). Of these, 258 and 533 sequences were available and downloaded from the MRC-CLIMB server at the time of running the analysis, respectively. Of these available genomes, 224 and 522 passed sequencing quality control thresholds (described in Materials and methods), respectively. This yielded the final analysis set of 700 high-coverage genomes from care home residents (representing 292 care homes): 197 genomes sequenced on site by nanopore and 503 sequences at WSI by Illumina. * 193 care homes were registered with the CQC as being residential homes without nursing care, referred to as ‘residential homes’ in main text, and 144 had nursing care available, referred to as ‘nursing homes’. ** Samples were selected for nanopore sequencing on site if they were inpatients or healthcare workers at Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust (CUH), where we prioritised rapid turnaround time to investigate hospital-acquired infections, plus a randomised selection of other East of England samples to provide broader genomic context to the CUH cases. The remaining samples not selected for nanopore sequencing on site, where available, were sent to WSI for sequencing.