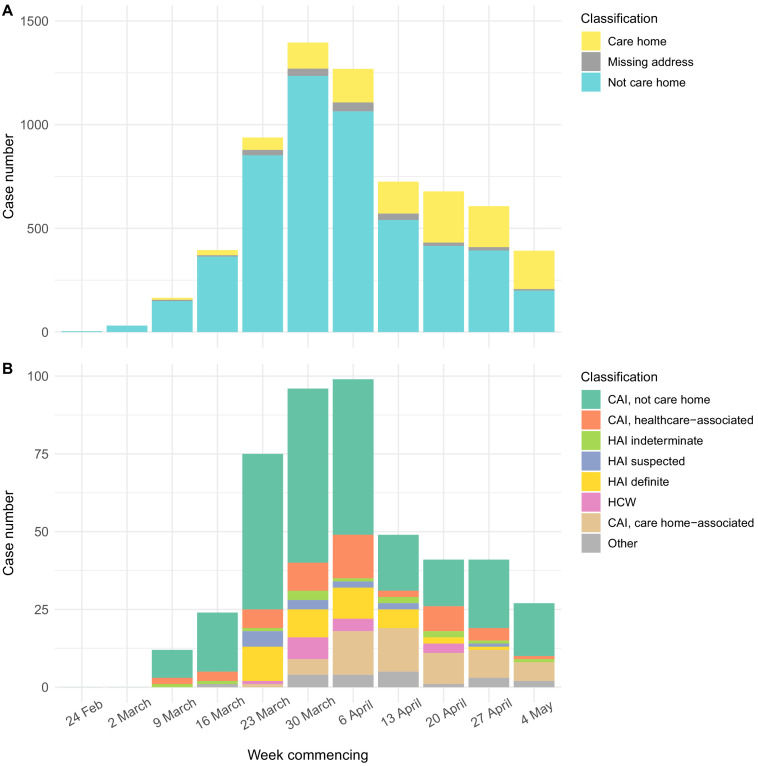
Figure 3. Epidemic curves for EoE and CUH showing care home residents.
Number of positive cases per week over the study period for different infection sources, for all samples tested from EoE at the Cambridge PHE laboratory (A), or those tested at CUH acute medical services (B). Peak of the epidemic for samples tested at the Cambridge PHE laboratory and CUH acute medical services were weeks commencing 30th March and 6th April, respectively. UK lockdown started 23rd March 2020. In both settings, a prolonged right-hand ‘tail’ was observed as case numbers gradually fell. The relative proportion of cases admitted from care homes increased over this period for both sample sets, while the contribution of general community cases fell more quickly. However, interpreting these trends is confounded by the changing profile of COVID-19 testing nationally and regionally. If the patient address was missing, and they were not a HCW, then the care home status was undetermined. CAI = Community Acquired Infection; EoE = East of England; HAI = Hospital Acquired Infection; HCW = Healthcare Worker; ‘Other’ mainly comprise inpatient transfers from other hospitals to CUH for which metadata was lacking to determine the infection category. CAI was considered ‘healthcare-associated’ if there had been healthcare contact within 14 days of first positive swab. The three categories of HAI were defined based on the difference in days between admission and first positive swab, reflecting increasing likelihood of hospital acquisition: indeterminate = 3–6 days; suspected 7–14 days; definite >14 days (as used in Meredith et al., 2020).