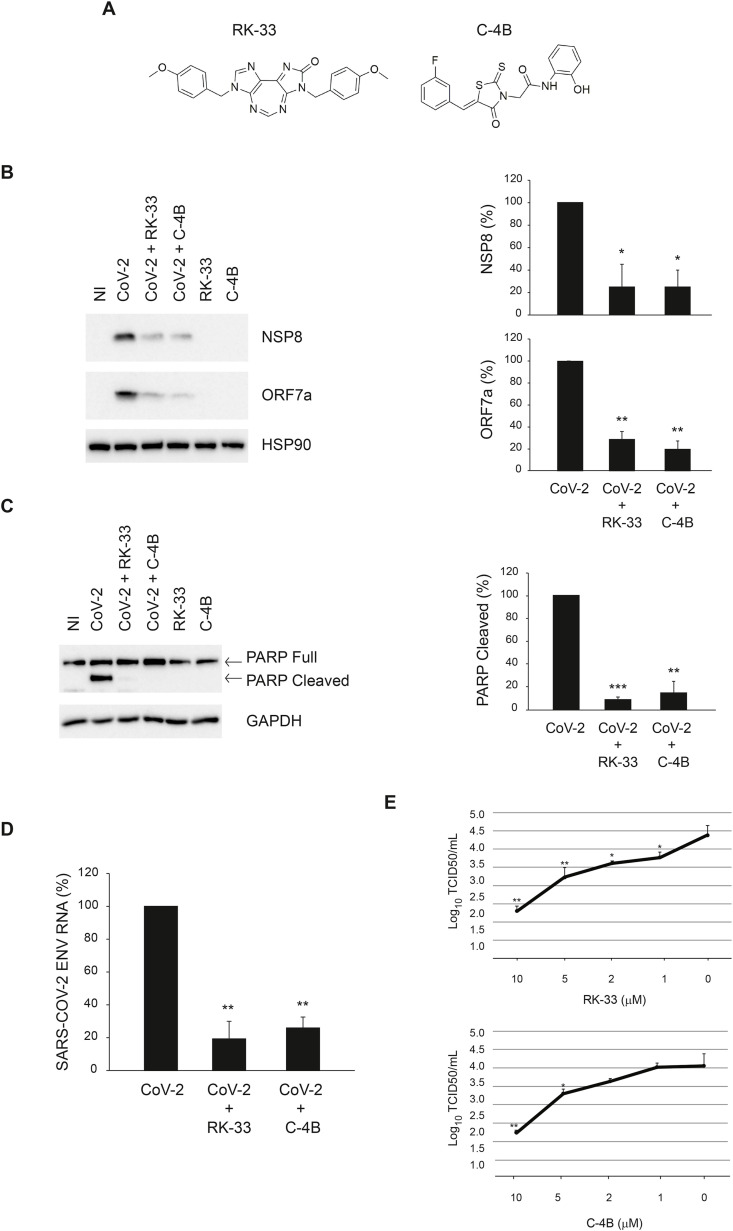
Fig. 4.
Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infection by RK-33 and C–4B in Vero E6 cells. A) Chemical structures of DDX3X inhibitors. B-D) Vero E6 cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 at MOI 0.001 and, at the end of the adsorption period, were treated with RK-33 10 μM, C–4B 10 μM or left untreated, as indicated. At 24 h post infection, cells were harvested and assayed for the levels of SARS-CoV-2 NSP8 and ORF7a proteins (B) and intracellular RNA (D) by immunoblotting and RT-qPCR, respectively. In addition, at 48 h post infection, PARP cleavage was monitored by immunoblotting to evaluate the level of cell death in infected cells (C). HSP90 and GAPDH were included as loading controls. The accompanying graphs report means ± SD of normalized values from three independent experiments. * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.01, *** = p < 0.001. Protein and viral RNA levels are reported as fold changes with respect to the amount detected at 24h post infection (p.i.). E) Vero E6 cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 at MOI 0.001. At the end of the adsorption period, cells were treated with RK-33 or C–4B 10 μM, 5 μM, 2 μM, 1 μM or left untreated. Cells and culture media were collected at 24h post infection and subjected to limiting dilution assay on Vero E6 cells. Infectious viral titers are expressed as mean ± SD of Log10TCID50/ml. * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.01. NI: non-infected. CoV-2: SARS-CoV-2.