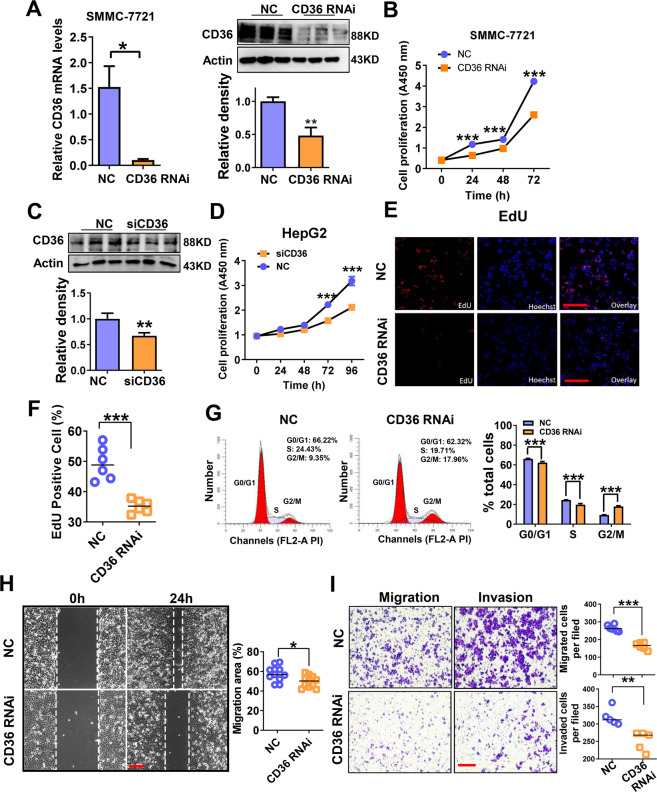
Fig. 2. CD36 knockdown has the negative impact on the proliferation, migration, and invasion of HCC cells.
CD36-knockdown (CD36 RNAi) cell line was established by transfecting CD36 shRNA lentiviral construct and targeting sequence 5′-GGCTGTGTTTGGAGGTATT CT-3′ or scrambled shRNA lentivirus as control (NC) to SMMC-7721 cells. A The knockdown efficiency of CD36 in SMMC-7721 cells was detected by real-time PCR and western blotting (n = 3). B The proliferation of the control and CD36 RNAi cells in SMMC-7721 cells was measured by CCK-8 assay (n ≥ 5). C The knockdown efficiency of CD36 in HepG2 cells was detected by western blotting (n = 3). D The proliferation of the control and CD36 RNAi cells in HepG2 cells was measured by CCK-8 assay (n ≥ 5). E The proliferation of the control and CD36 RNAi cells in SMMC-7721 cells was measured by EdU assay, the Edu-positive cells were shown in the following (F) (n ≥ 5). G Cell cycle analysis was performed after culture for 48 h using flow cytometer (n = 3). H Scratch-wound cell migration assay of the control and CD36 RNAi cells (n = 5). I Cell migration and invasion ability was evaluated by transwell assay (n = 5). Cell number refers to the average number ± SEM per field counted at ×200 magnification. *P < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 compared with the NC group. Bar = 100 μm (C, E, F). P-value was calculated using Student’s t-test.