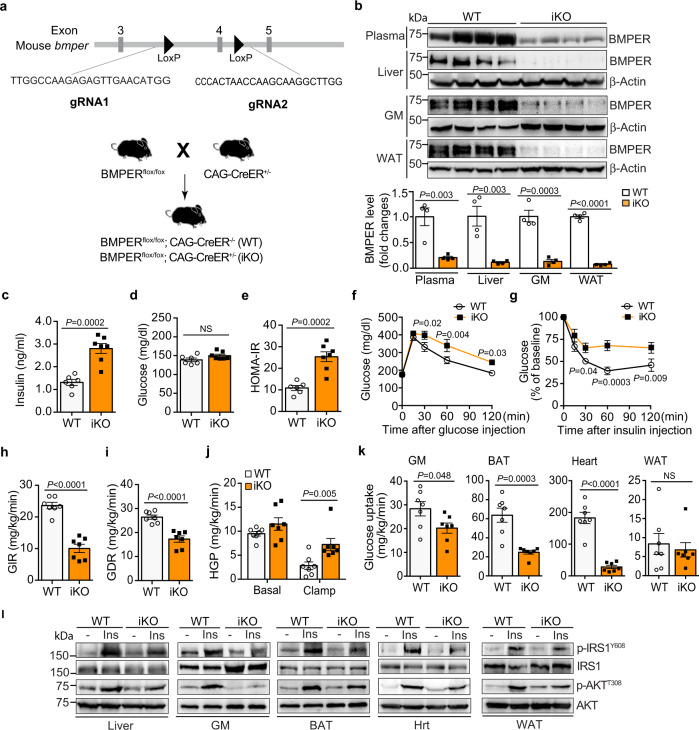
Fig. 1. BMPER depletion causes mice to develop hyperinsulinemia, glucose intolerance, and insulin resistance.
a The generation of the BMPER iKO mouse model. The gRNA-guided CRISPR/Cas9 strategy was used for targeted deletion of bmper gene. b BMPER depletion was examined with Western blotting. c–e Fasted insulin and glucose, HOMA-IR. f, g Glucose and insulin tolerance tests. h Glucose infusion rate (GIR). i Glucose disposal rate (GDR). j, k Hepatic glucose production (HGP; j) and glucose uptake in peripheral tissues (k) were analyzed with hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps. l Insulin signaling was blunted in BMPER iKO mice. Insulin (Ins, 0.5 h) was injected (i.p.) into BMPER iKO and WT mice. Indicated tissues were used for Western blotting. GM gastrocnemius muscle, BAT brown adipose tissue, WAT white adipose tissue, Hrt heart. WT, BMPERflox/flox; CAG-CreER–/–. iKO, BMPERflox/flox; CAG-CreER+/–. n = 4 mice (b), 6 mice (c–e WT), 7 mice (c–e iKO), 7 mice (f, h–k) and 5 mice (g). Data are presented as mean values ± SEM. NS not significant. Analysis was two-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD multiple comparison test (for f, g, j) or unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test (for b–e, h, i, k).