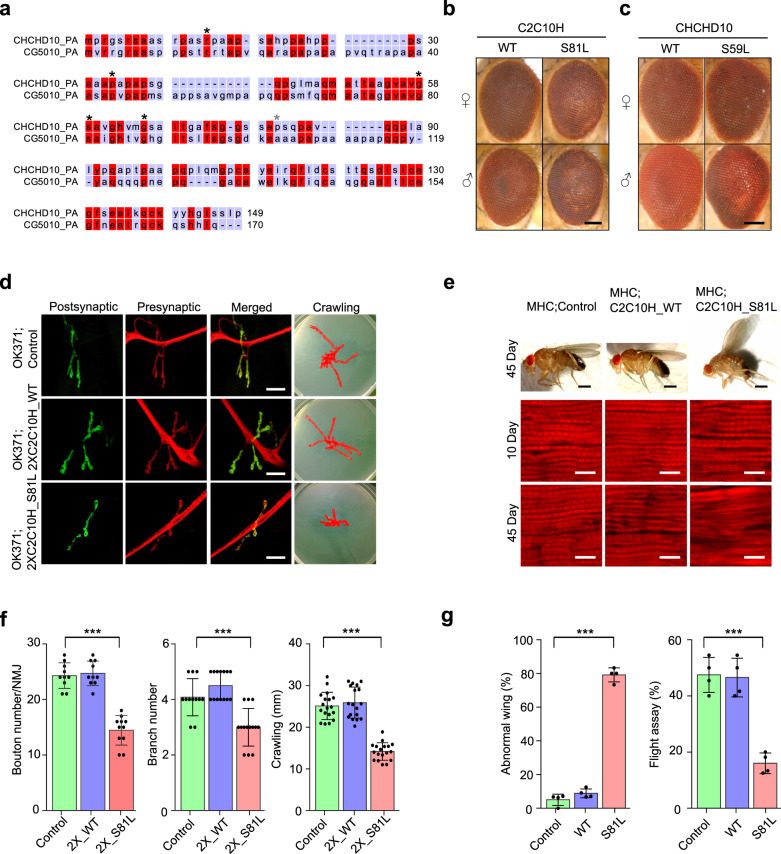
Fig. 1. C2C10HS81L is toxic in Drosophila eyes, neurons, and muscles.
a Protein sequence alignment of human CHCHD10 and Drosophila C2C10H (CG5010). Disease-causing sites (asterisk) are conserved between human CHCHD10 and Drosophila C2C10H. b C2C10HS81L (representative images from two independent experiments) and c human CHCHD10S59L cause age-dependent mild rough eye phenotypes in 40-day-old flies (representative images from two independent experiments). Scale bar = 200 μm. d Representative images of neuromuscular junctions and crawling traces from the genotypes indicated (see below for statistical analysis). Scale bar = 20 μm. e Adult thoraxes dissected to expose longitudinal indirect flight muscles and stained with phalloidin–Alexa Fluor 594. Flies expressing C2C10HS81L in muscles under control of MHC-GAL4 exhibit disrupted sarcomere structures. Scale bar = 0.5 mm (fly) and 10 μm (muscle). f Expression of C2C10HS81L in motor neurons results in small synapses, with reduced bouton and branch numbers and defective locomotive activity assessed by the crawling behavior of third-instar larvae. Data are mean ± SD (one-way ANOVA and post hoc Dunnett test, two-sided, ***p = 5.3e − 10, 0.0002 and 3.8e − 14 for bouton number (n = 10–11), branch number (n = 12–14), and crawling distance (n = 18) from three independent experiments, respectively). g Expression of C2C10HS81L in muscle tissues causes abnormal wing postures and locomotor defects assessed by flight ability. Data are mean ± SD (one-way ANOVA and post hoc Dunnett test, two-sided, ***p = 4.3e − 10, 5.5e − 05 for abnormal wing posture, flight assay, respectively; n = 4 with >40 flies).