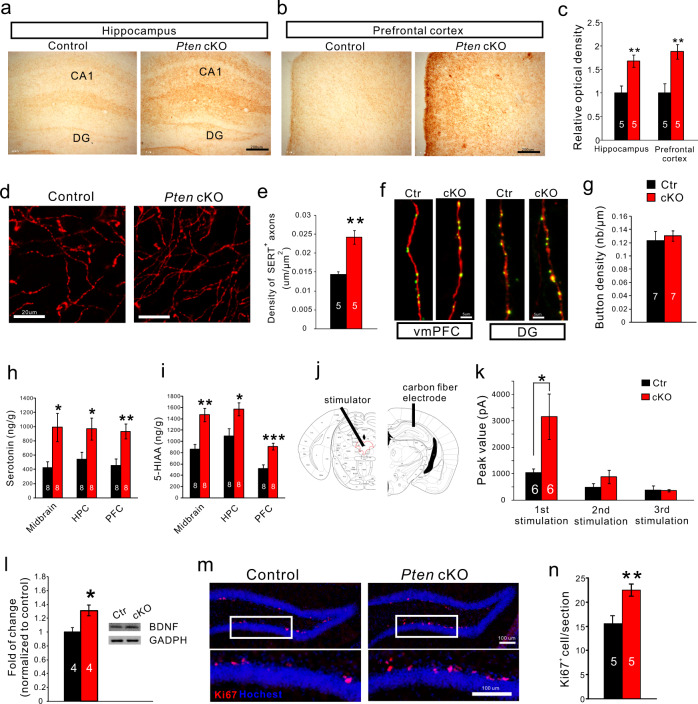
Fig. 4. The increase of 5-HT innervation and axonal release of 5-HT in Pten cKO brain.
a, b. SERT+ axons/terminals visualized with diaminobenzidine as chromogen in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex in control and Pten cKO mice. Scale bars = 200 μm. c SERT+ axons/terminals shown by optical density are increased in the two regions of Pten cKO mice relative to control. d, e High magnification of SERT immunostaining shows individual axons/terminals in the prefrontal cortex (d) and comparison of the density of SERT+ axons/terminals there (e). f Images showing synaptophysin-fused EGFP-labeled buttons within tdTomato-labeled 5-HT axon terminals in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) and dentate gyrus (DG). g. The density of EGFP-labeled buttons within tdTomato-labeled terminals in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex is similar between Pten cKO and control mice. Scale bars = 5 μm. h, i 5-HT, and its metabolite 5-HIAA are increased in the midbrain, hippocampus (HPC), and prefrontal cortex (PFC) of Pten cKO mice relative to control. j, k Electrical stimulation of the dorsal raphe nucleus elicits increases of 5-HT release in the hippocampus of Pten cKO mice compared with controls. l BDNF levels are increased in the hippocampus of Pten cKO mice. m, n The increase of Ki67+ cells in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus of Pten cKO mice compared with controls. Scale bars = 100 μm. Numbers of animal used are indicated. All the data are presented as the mean ± s.e.m. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.