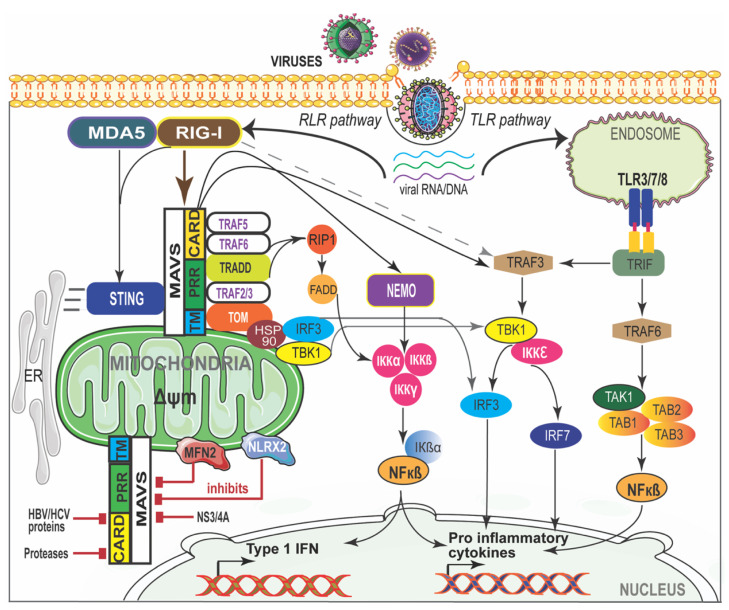
Figure 2.
RIG-I/MDA-5 and MAVS interaction in viral disease. The cytosolic viral RNA/DNA is recognized by the RLR and/or TLR pathways. RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs) and MDA-5 activate MAVS through CARD and recruit signaling molecules to induce canonical nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). NF-κB translocates into the nucleus and initiates pro-inflammatory cytokine gene expression. MAVS activates the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) and further mediates the activation of TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) which phosphorylates interferon regulatory factor (IRF) signaling factors IRF-3 and IRF-7. IRF-3 then translocates into the nucleus and induces type I interferon (IFN) genes. NS3-4A, mitofusin 2 (MFN2), and NLR family member X1 (NLRX1) inhibit MAVS by preventing the formation of the MAVS–IKKi signaling complex. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) X protein promotes polyubiquitin conjugation of MAVS. ER—endoplasmic reticulum; MAM—mitochondria-associated membrane.