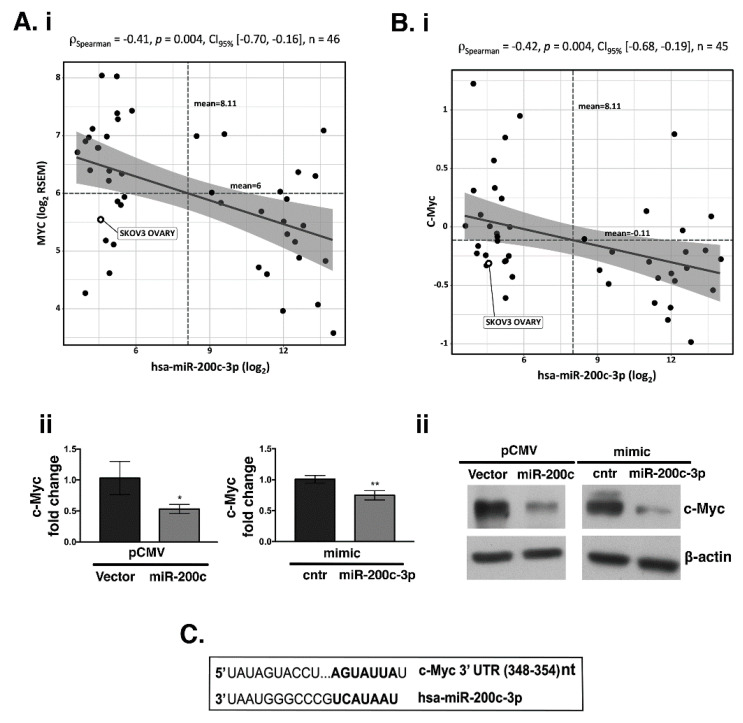
Figure 3.
Transcriptional and translational regulation of c-Myc by miR-200c-3p (A) (i): RNA-sequencing data retrieved from CCLE data portal of 46 cell lines showed an inverse correlation between MYC gene and miR-200c-3p. (ii): RT-qPCR was used to verify the decrease of c-Myc transcript in both, stably transfected (pCMV V. and miR-200c) and transiently transfected (mimic cntr and mimic miR-200c-3p). SD± shows the mean of three independent experiments and in technical triplicates. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, (B) (i): Reverse Phase Protein Arrays (RPPA) extracted from CCLE data portal in 45 OC cell lines as in A, showed that c-Myc protein is inversely correlated with miR-200c-3p. Spearman correlation analysis was reported, with statistical significance (p < 0.05). Confidence intervals at 95% are also reported. (ii): WB analysis of c-Myc expression in stably transfected (pCMV V. and miR-200c) and transiently transfected (mimic control: cntr and mimic miR-200c-3p). (C): TargetScan v7.1 prediction shows a miR-200c-3p binding site (seed sequence) in the 3′UTR of c-Myc from 358 to 354 nucleotides (top).