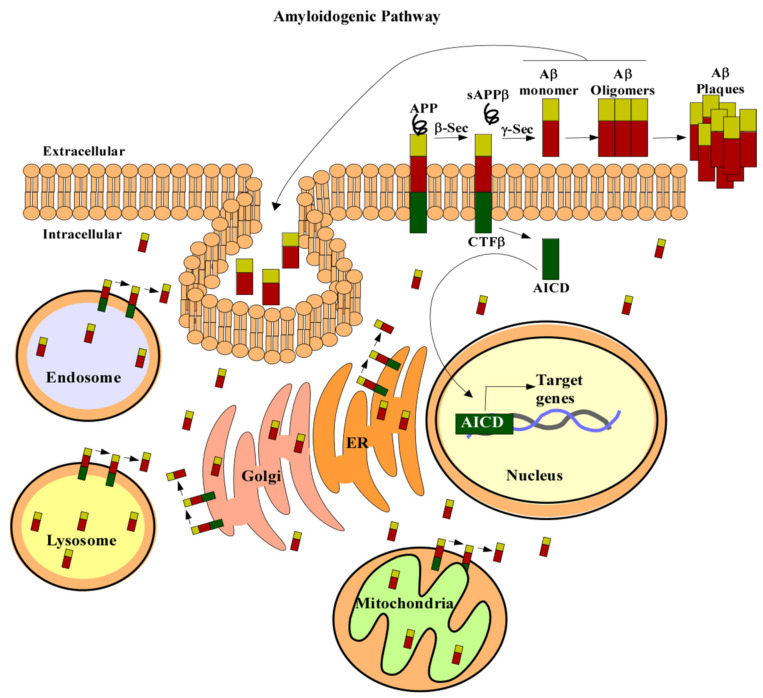
Figure 1.
APP processing. In the amyloidogenic pathway APP (in green red and gold) is cleaved by β secretase to produce a soluble form of APP, sAPPβ. Then, γ-secretase cleaves the remaining amino acid protein CTFβ to produce Aβ (red and gold) and AICD (green). Aβ can then form oligomers and plaques which are characteristic of AD. AICD can translocate to the nucleus (beige) and regulate gene expression (DNA is in grey and blue). APP can also be localized to the trans-Golgi network (pink), ER (orange), endosomal (blue), lysosomal (yellow), and mitochondrial membranes (green). Aβ liberation can occur wherever APP and the β- and γ-secretases are localized. Aβ can also be taken up by the cell to form intracellular pools. Abbreviations: amyloid precursor protein (APP), secreted APP derivative (sAPPβ), amyloid beta (Aβ), β-Secretase-Derived C-Terminal Fragment (CTFβ), APP intracellular domain (AICD), β-APP-site cleaving enzyme (β-Sec), γ-Secretase (y-Sec), ER (endoplasmic reticulum).