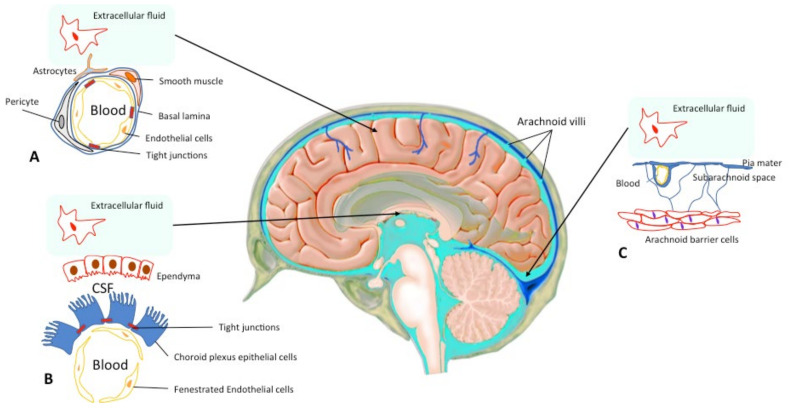
Figure 1.
Central Nervous System Barriers. The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is present between the cerebral capillaries and the brain parenchyma (A). Endothelial cells with tight junctions, basal lamina, pericytes and astrocyte endfeet separate the blood compartment from the extracellular fluid. The blood–cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) barrier lies at choroid plexus in the lateral, 3rd, and 4th ventricles of the brain (B). The arachnoid barrier (C), close to the sagittal sinus, is formed by a multilayer epithelial structure with tight junctions. Arachnoid villi cross the dura, project into the sinus, and drain CSF into the blood (according to Abbott et al. 2010; Haines DE 1991 [2,3]).