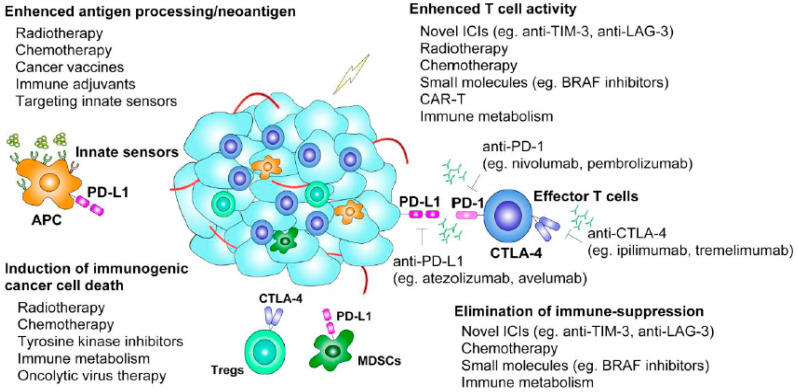
Figure 2.
Summary of prospective combination strategies with checkpoint inhibition. Currently used monoclonal antibodies targeting PD-L1 (atezolizumab, avelumab), PD-1 (nivolumab, pembrolizumab), and CTLA-4 (ipilimumab, tremelimumab) as well as combination strategies involving various mechanisms for enhancing the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are presented. Novel immunotherapies, including oncolytic virus therapy and therapies targeting innate sensors, can either directly kill tumor cells or facilitate the presentation of tumor antigens in the generation of tumor-specific T cells. APC, antigen-presenting cell; BRAF, B-Raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine-protein kinase; CAR-T cell, chimeric antigen receptor T cell; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; LAG-3, lymphocyte-activation gene 3; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand 1; TIM-3: T cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain-containing molecule 3; Tregs, regulatory T cells.