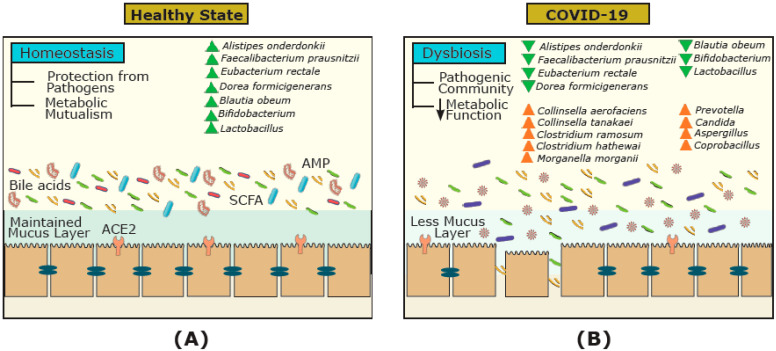
Figure 3.
The gut microbial ecosystem and underlying mechanisms involved in COVID-19 infection. The gut microbiota of (A) healthy individuals, and (B) COVID-19-infected individuals. In healthy individuals, the gut harbors diverse communities and metabolites (e.g., short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and bile acids) that vary from the gut microbial communities of COVID-19-infected individuals. During COVID-19, the dysbiosis of the gut microbial ecosystem, the reduction in metabolites involved, and downregulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors can affect the immune system (e.g., reduction in antimicrobial peptides (AMPs)) and worsen conditions.