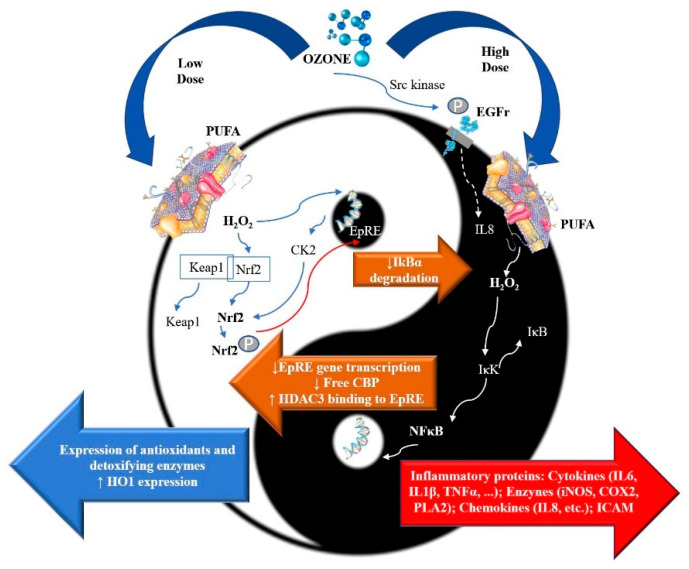
Figure 1.
Hypothetic effects of ozone mediators on Nrf2 and NfκB pathways. After administration, ozone reacts with biomolecules, including polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) or plasma membrane, producing hydroperoxides, aldehydes, and H2O2 [60]. H2O2 can enter the cytoplasm of mononuclear cells and modulate nuclear factor NF-κB/Nrf2 pathways. Casein kinase 2 (CK2), CREB binding protein (CBP), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), Electrophile-responsive elements (EpRE), Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFr), Heme-oxygenase-1 (HO-1), Histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3), Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), Interleukin-1β (IL-1 β), Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Interleukin-8 (IL-8), Intracellular adhesion molecule (ICAM), IκB kinase (IKK), Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1), Nuclear erythroid 2 related factor 2 (Nrf2), Phospholipase A2 (PLA2), Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α).