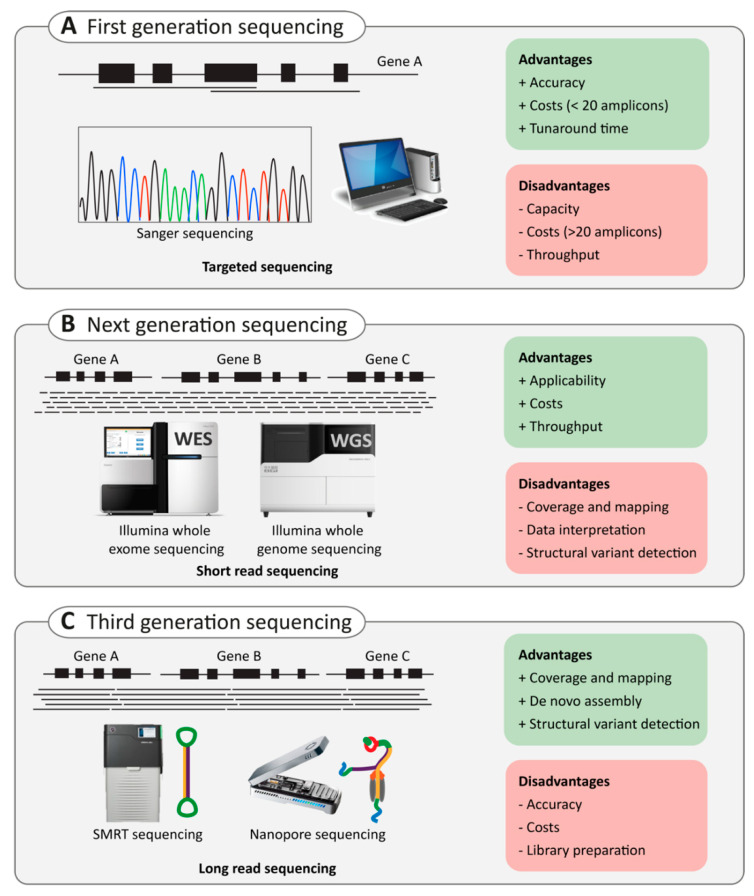
Figure 3.
Comparison of conventional Sanger, next-generation, and third-generation sequencing. (A) schematic representation of (A)) first generation sequencing (Sanger sequencing), (B) next generation sequencing (e.g. Illumina whole-genome sequencing (WGS) and whole-exome sequencing (WES)) and (C) third-generation sequencing (e.g. SMRT sequencing as performed by Pacific Biosciences (PacBio) and nanopore sequencing by Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT)). For each technique, advantages (green) and disadvantages (red) are provided.