Figure 1.
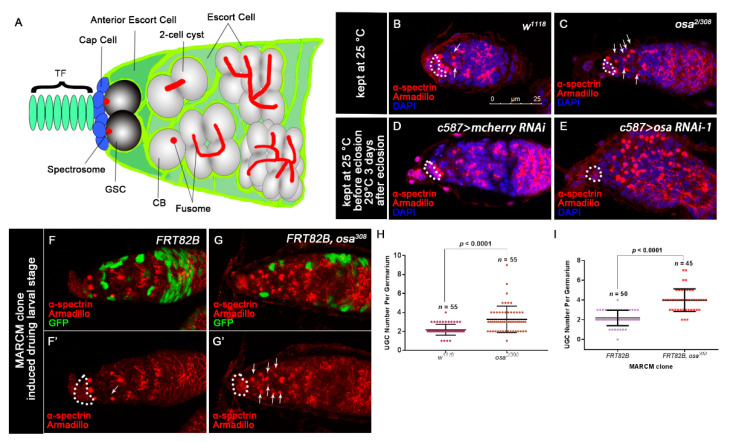
Disruption of Osa results in the accumulation of round fusome-containing germ cells. (A) Schematic of a Drosophila germarium. (B–E) Germaria stained for α-spectrin (red), Armadillo (red) and DAPI (blue). CpCs are indicated by white dashed circles. (B) The wild-type (WT) (w1118) germarium contains three germline stem cells (GSCs) and two cystoblasts (CBs, indicated by white arrows). (C) The osa2/308 germarium displays an expanded number of UGCs outside the GSC niche (indicated by white arrows). The control germarium (D) contains a normal number of CBs. The osa KD germarium (E) displays an expanded number of UGCs. c587 > osa RNAi-2 gives a similar phenotype and is not shown in the figure. (F–G’) MARCM clones were stained for α-spectrin (red), Armadillo (red), and GFP (green). Clonal cells are marked by GFP. CpCs are indicated by white dashed circles. (F,F’) A germarium containing control clones displaying normal number of CBs (indicated by white arrows). (G,G’) A germarium containing the escort cell (EC) mutant for the osa308 exhibiting an expanded number of UGCs (indicated by white arrows). (H) A graph showing the quantification of UGCs for each germarium. (I) A graph showing the quantification of UGCs for each germarium. Error bars are presented as the Mean ± SD. Several compressed z-sections are shown in (B–G’). The scale bar is shown in (B).