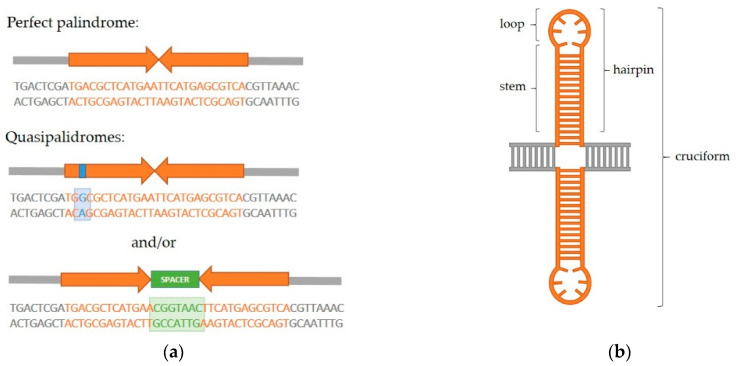
Figure 1.
Palindromic sequences and secondary structures. (a) Types of palindromic sequences. A perfect palindrome consists of two identical inverted repeats adjacent to one another. A quasipalindrome can contain mismatches between the two inverted repeats and/or a central spacer region. (b) Palindromic sequences can form secondary structures due to intrastrand base pairing. In ssDNA, the hairpin structure, consisting of a stem and a loop, is formed. Two hairpins, one across from the other in a dsDNA, together constitute a cruciform structure.