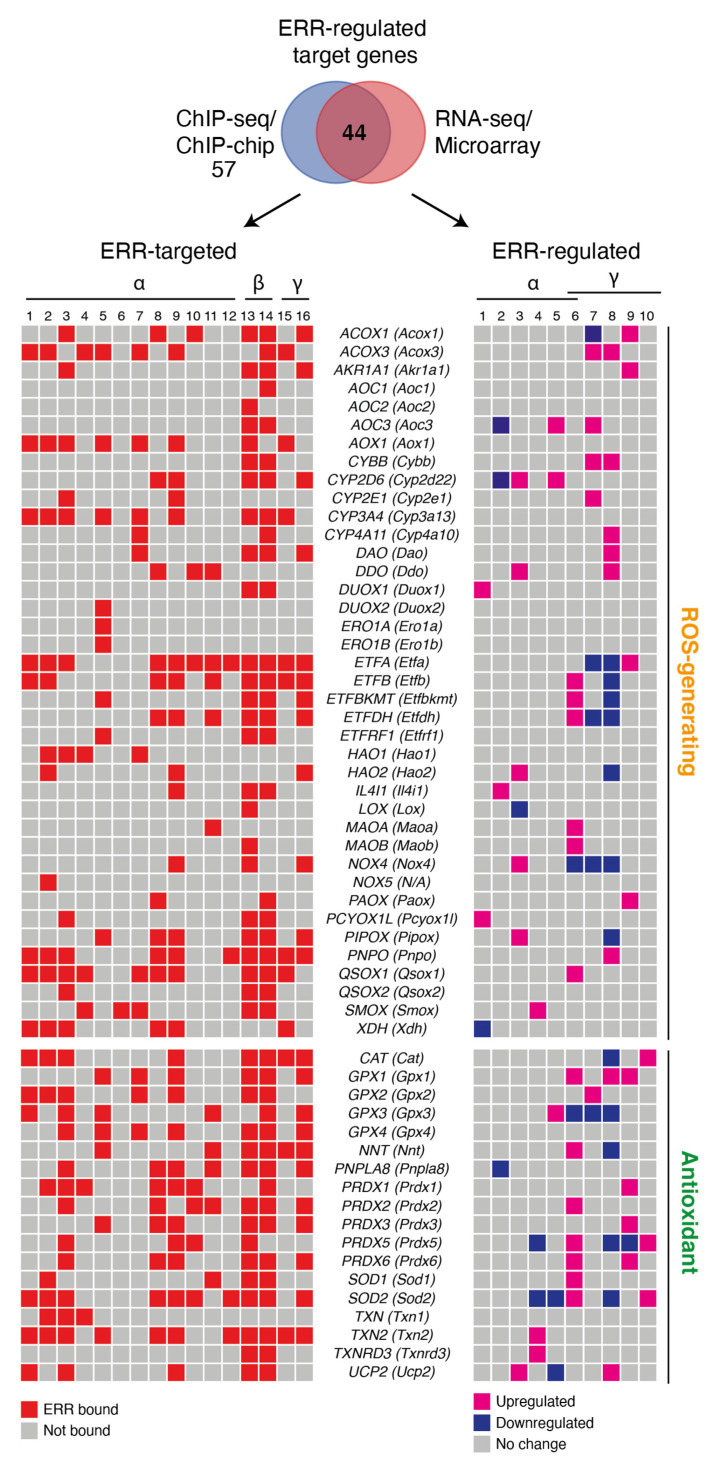
Figure 1.
ERR-targeted enzymes implicated in ROS metabolism. Schemes follow the same formatting. Both human and mouse gene names are shown, the latter in parentheses. Genes implicated in both ROS generation and antioxidant response were manually curated from the literature and only genes found targeted (58 out of 63) by the estrogen-related-receptors (ERRs) in at least one cell or tissue from ChIP-based technologies are shown in a heatmap representation. Of the 58 ERR-targeted genes, those found differentially regulated by the ERRs based on available RNA-seq and microarray datasets are shown in a heatmap representation. Red boxes indicate ERR-occupied genes. Pink and blue boxes indicate upregulated and downregulated genes, respectively, that are ERR-regulated. For ChIP-seq, genes with binding peaks within ±20 kb from the transcriptional start sites were considered. For ChIP-chip, genes with a cutoff of p < 0.001 were considered. The ERR-targeted datasets shown are ordered as follows: (1) BCa-BT474 ERRα ChIP-seq (untreated) [48]; (2) BCa-BT474 + AICAR ERRα ChIP-seq (AICAR-treated) [48]; (3) BCa-SKBR3 ERRα ChIP-seq (untreated, serum-starved) [11]; (4) BCa-MCF7 ERRα ChIP-seq (untreated, serum-starved) [Deblois G, unpublished]; (5) B lymphocytes-GM12878 ERRα ChIP-seq [88]; (6) CRC-LoVo ERRα ChIP-seq [89]; (7) HCC-HepG2 ERRα ChIP-seq [90]; (8) mouse liver ERRα ChIP-chip [71]; (9) mouse liver ERRα ChIP-seq [34]; (10) mouse kidney ERRα ChIP-chip [91]; (11) mouse skeletal muscle ERRα ChIP-chip (gastrocnemius and soleus) [Dufour CR, unpublished]; (12) mouse frontal cortex ERRα ChIP-seq [92]; (13) mouse ESC ERRβ ChIP-seq [93]; (14) mouse ESC ERRβ ChIP-seq [94]; (15) BCa-BT474 ERRγ ChIP-seq [12]; (16) mouse kidney ERRγ ChIP-seq [95]. The ERR-regulated datasets shown are ordered as follows: (1) BCa-SKBR3 siERRa vs. siCtrl microarray [11] cutoff: p < 0.05; (2) BCa-SKBR3 siERRa vs. siCtrl microarray (untreated, serum-starved) cutoff: p < 0.05 [11]; (3) mouse kidney ERRα KO vs. WT (basal) microarray [91] cutoff: FC 1.2 and p < 0.05; (4) mouse skeletal muscle ERRα KO vs. WT (basal) microarray (gastrocnemius) [96] cutoff: FC 1.2 and p < 0.05; (5) mouse heart ERRα KO vs. WT (basal) microarray [19] p < 0.05; (6) mouse cardiac ventricles ERRα/γ DKO vs. WT (basal) microarray [97] cutoff: FC 1.5 and p < 0.05; (7 and 8) mouse RECs ERRα KO vs. WT (basal) RNA-seq in 3-month (7) or 3-week (8) old mice [95] cutoff: logFC1.5 and p adjusted < 0.05; (9 and 10) PCa-LNCaP siERRγ vs. siCtrl basal (9) or R1881 (10) (synthetic androgen) microarray [98] p < 0.05. Abbreviations used: AICAR, 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide); BCa, breast cancer; CRC, colorectal cancer; Ctrl, control; DKO, double knockout; ESC, embryonic stem cell; FC, fold-change; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; KO, knockout; N/A, non-applicable; PCa, prostate cancer; REC, renal epithelial cells; WT, wild type.