Figure 2.
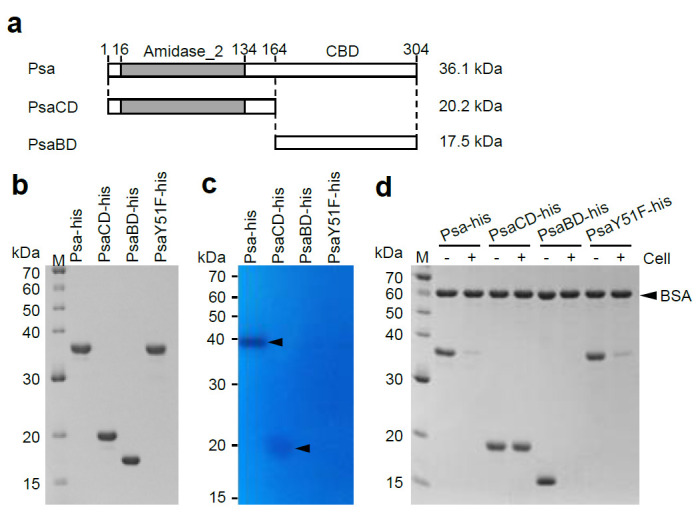
SDS-PAGE analysis, zymography analysis, and binding analysis of Psa-his, PsaCD-his, PsaBD-his, and PsaY51F-his. (a) Schematic diagrams of Psa, PsaCD, and PsaBD are shown Psa has an N-terminal catalytic domain (CD) of the amidase_2 family (indicated by gray bar) and a novel C-terminal cell wall-binding domain (CBD). These proteins were expressed and purified with a histidine-tag (MNHKVHHHHHH) fused to the N-terminus. The molecular weights of each histidine-tagged protein are shown on the right of the corresponding horizontal bar. (b) Purified Psa-his, PsaCD-his, PsaBD-his, and PsaY51F-his (1 μg each) were subjected to 12.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The gel was stained with Coomassie blue R. (c) Zymography analysis was carried out according to the Materials and Methods. Purified Psa-his (0.5 μg), PsaCD-his (2.0 μg), PsaBD-his(2.0 μg), and PsaY51F-his (0.5 μg) were electrophoresed in a 12.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gel containing 20 OD600 of heat-inactivated and SDS-treated C. perfringens HN1314 cells. The arrowheads indicate cell lysis. (d) Binding activity was measured according to the Materials and Methods. The purified protein and non-binding internal standard, bovine serum albumin (BSA), were combined with (+) or without (−) C. perfringens HN1314 cells; the mixtures then were centrifuged, and the resulting supernatants were analyzed by 12.5% SDS-PAGE.
