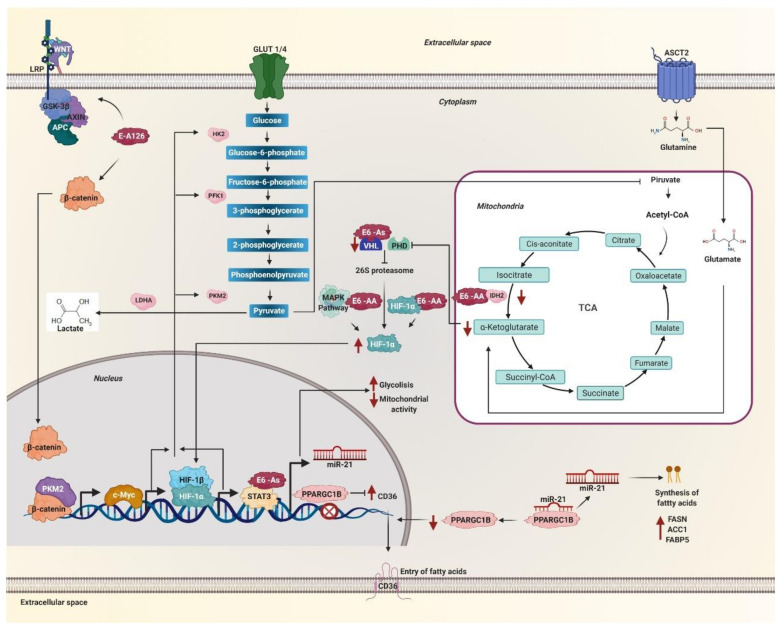
Figure 3.
Metabolic reprogramming is mediated by HPV 16 E6 variants through c-Myc, hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α, WNT, and miR-21. The E6 variant E-A126 with the R8Q mutation promotes the glycolytic pathway by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Variants of the AA sublineage activate the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) pathway that increases HIF-1α levels. The protein β-catenin translocates to the nucleus accompanied by PKM2 and induces the expression of c-Myc. These variants also decrease the levels of the isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH2) enzyme necessary to obtain α-ketoglutarate, one of the substrates of the prolyl-4-hydroxylases (PHDs) enzymes. On the other hand, the As sublineage variants decrease the von Hippel Lindau (VHL) ubiquitin ligase levels, both enzymes are necessary for HIF-1α to be degraded via the 26S proteasome. Therefore, the variants of the AA and As sublineages increase the levels of HIF-1α, avoiding its degradation via the proteasome. Consequently, HIF-1α stabilizes and translocates to the nucleus. Both HIF-1α and c-Myc increase the levels of glycolysis enzymes such as hexokinase 2 (HK2), phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK1), pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2), lactate dehydrogenase A (LDH-A), as well, lactate levels increase. The STAT3 activator increases glycolysis, decreases mitochondrial activity and allows the transcription of miR-21, which is also positively regulated by variants of the As sublineage. MiR-21 inhibits the PPARGC1B messenger. The levels of the CD36 transcriptional repressor PPARGC1B decrease and allow the expression and translocation of CD36. In this way, miR-21 regulates the entry and synthesis of fatty acids in the cell by the effect of the variants of the AA and As sublineages.