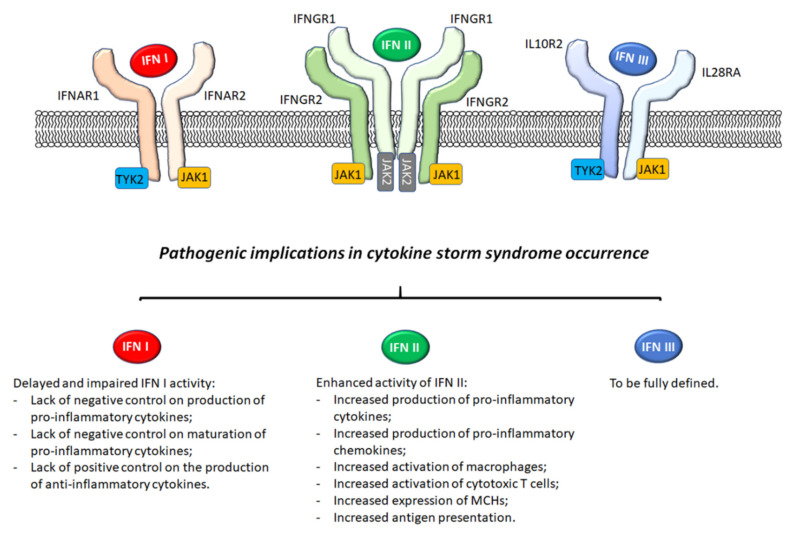
Figure 1.
Pathogenic implications of IFNs in a cytokine storm syndrome occurrence. Type I IFNs bind to the IFNAR complex, consisting of two different chains, IFNAR1 and IFNAR2. Type II IFN activates the IFNGR, which is composed of two different chains, IFNGR1 and IFNGR2, and type III IFNs signal through a receptor complex made up of IL28RA and IL10R2. The impairment of the functions of type I IFNs or its delayed response may be implicated in the development of a cytokine storm syndrome lacking the negative control of production and maturation of pro-inflammatory cytokines as well as lacking the positive control on the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines. The enhanced activity of IFN II results in occurrences of cytokine storm syndrome via increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines and the increased activation of macrophages and cytotoxic T cells. The role of IFN III in this context has yet to be fully defined. Abbreviations: IFN: Interferon; IFNAR: interferon-alpha/beta receptor; IFNGR: interferon-gamma receptor; IL28RA: interleukin 28 receptor, alpha subunit; IL10R2: interleukin 10 receptor 2; TYK2: tyrosine kinase 2; JAK 1: Janus kinase 1; JAK 2: Janus kinase 2.