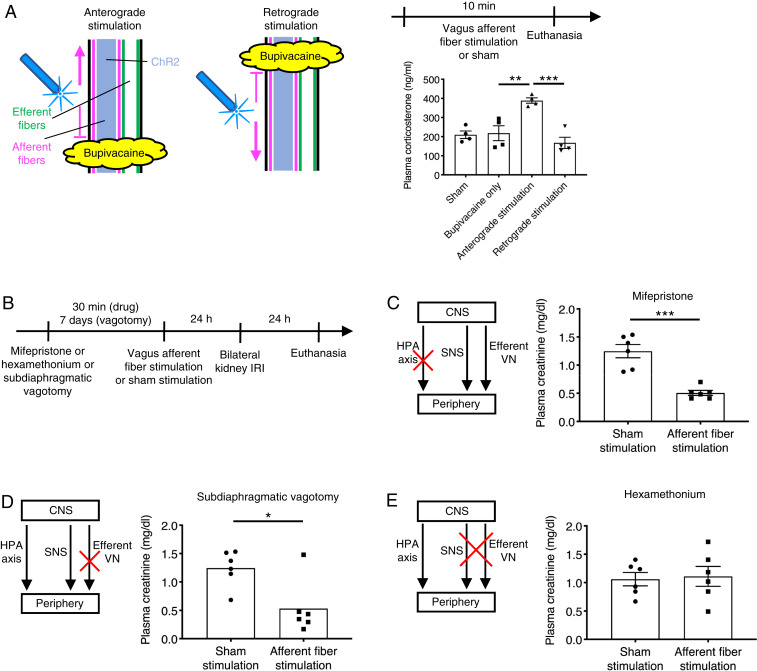
Fig. 4.
Sympathetic nervous system plays a predominant role in kidney protection by vagus afferent fiber stimulation. (A) Plasma corticosterone levels immediately after vagus afferent fiber stimulation or sham stimulation (by setting the laser output to zero) for 10 min in Vglut2-ChR2 mice with illustration depicting optogenetic anterograde versus retrograde VNS. Bupivacaine was directly applied to the left cervical vagus nerve to block nerve conduction, and blue laser was applied to the central or distal side of the anesthetized area for anterograde or retrograde stimulation, respectively. (B) Timeline of experiments (C–E) for investigating which pathway among HPA axis, sympathetic nervous system (SNS), and efferent vagus nerve (VN) mediates the protective effect of vagus afferent fiber stimulation against kidney IRI. (C–E) Plasma creatinine 24 h after bilateral kidney IRI. Mice were given mifepristone (corticosterone receptor antagonist, C) or hexamethonium (ganglionic blocker, E) or underwent subdiaphragmatic vagotomy (D) before optogenetic vagus afferent fiber stimulation (Vglut2-ChR2 mice) or sham stimulation (same trains of laser light delivered to Cre-negative littermates). n = 4 in each group (A), and n = 6 in each group (C–E). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. When no error bar is shown, this is because the data were not normally distributed, and a nonparametric test was used. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test (A), unpaired two-sided Student’s t test (C and E), or two-sided Mann–Whitney test (D). CNS, central nervous system.