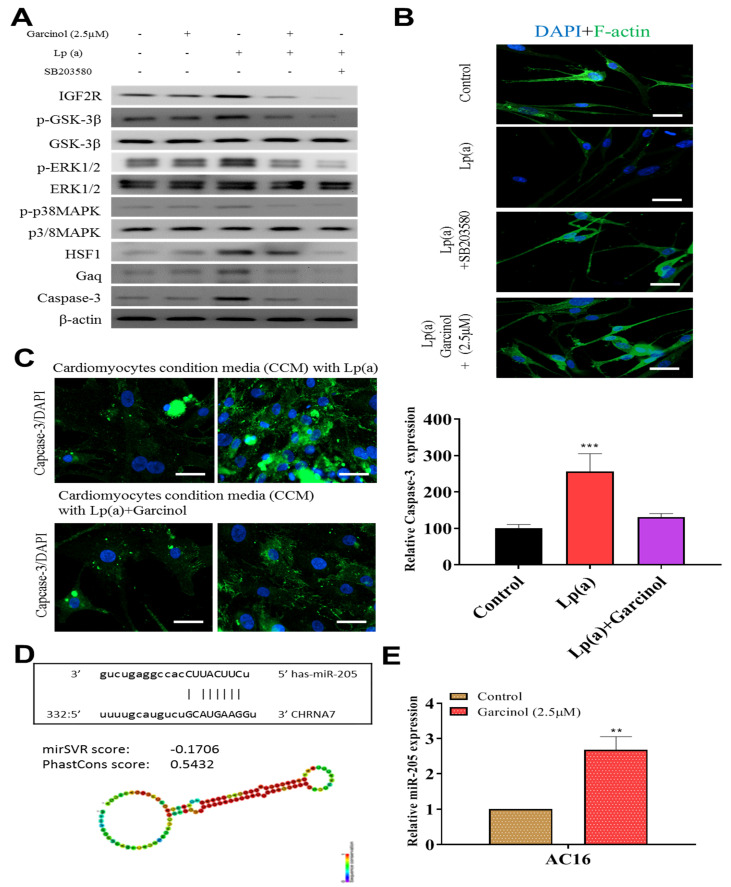
Figure 5.
Garcinol prevented apoptosis and inhibited insulin-like growth factor-II receptor (IGF2R) through inactivation of phosphorylation of GSK-3β/ERK/p38 MAPK in ventricular cardiomyocyte AC16 cells. (A) Western blot analysis revealed that Lp(a) upregulated the expression of MAPK signaling-related proteins including p-GSK-3β, p-ERK1/2 and p-p38 MAPK. Garcinol significantly inhibited the Lp(a)-induced phosphorylation of GSK-3β, ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK, but had no obvious effect on total ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK expression. (B) In the immunofluorescence analysis of F-actin polymerization, nuclei and F-actin were stained, respectively, with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue) and rhodamine-phalloidin (red orange). An overlay of the two fluorescent signals was shown (scale bars = 20 μm). (C) Left panel: representative images of caspase-3 activation in AC16 cells treated with cardiomyocytes condition media in the presence of Lp(a) for 24 h with and without garcinol. Right panel: quantification of relative caspase-3 activation. A substantial reduction in caspase activation, suggesting less apoptosis, was observed in garcinol treatment in comparison to Lp(a) only treatment. (D) The mir-Target prediction showed the 3′UTR sites of CHRNA7 targeted by miR-205. (E) qPCR analysis showed miR-205 expression was significantly upregulated by garcinol in comparison to control. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.