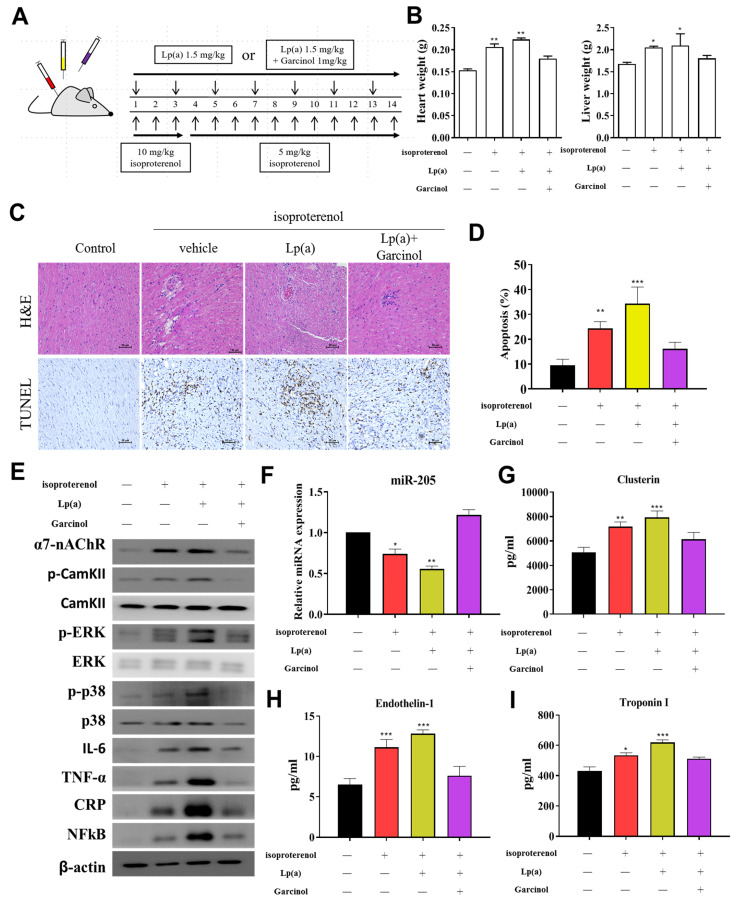
Figure 6.
Garcinol suppressed Lp(a)-induced myocardial apoptosis and inflammation in a mouse model of myocardial infarction. (A) The protocol for the induction of myocardial infarction in C57/B6 mice. (B) The heart and liver weight of the control group, and Lp(a) treated mice as compared to the garcinol treatment in mice. (C) H&E and transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining results of myocardium in the sham, Lp(a) and garcinol groups. (D) Quantitative analysis of percentage apoptosis. (E) Western blot showed a decrease in the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, CRP, NFκB, and phosphorylated CamKII/ERK/p38 MAPK by garcinol. β-actin was used as the loading control. (F) RT-qPCR analysis indicated that the relative miR-205 expression was significantly higher in mice treated with garcinol in comparison to Lp(a) group. (G–I) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) analysis results as compared to the treatment group, the significant reduction in the level of hemodynamic and cardiac function markers clusterin, endothelin-1 and troponin I. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.