Fig. 2.
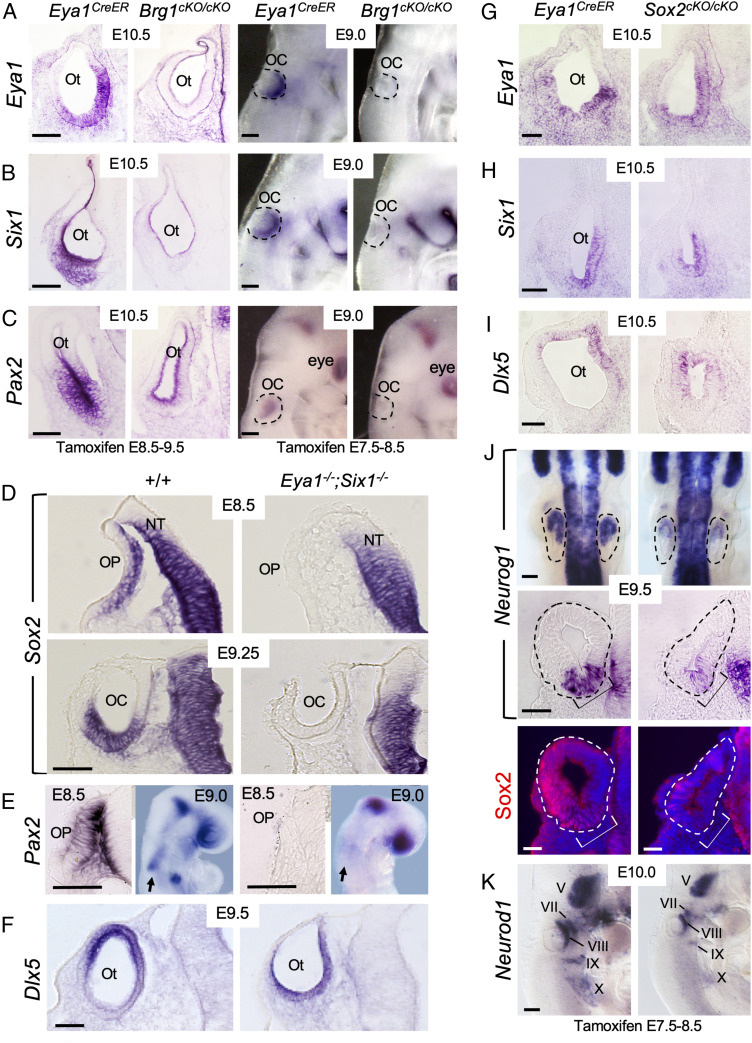
Brg1 is necessary for the expression of Eya1/Six1, both of which are necessary for the activation of Sox2 expression in otic ectoderm. Sections are transverse and dorsal is up. For whole-mount images, anterior is up. (A–C) Left panels are section views of otic vesicle (Ot) and Right panels are whole-mount lateral views of invaginating otic placode (OP)/cup (OC) (outlined by dashed lines) showing ISH for Eya1, Six1, and Pax2. Note that sections were cut from ISH embryos. (Scale bars, 50 μm.) (D) Section ISH for Sox2. Note that Sox2 expression in the neural tube (NT) was not affected. (Scale bar, 50 μm.) (E) Section (E8.5) and whole-mount (E9.0, lateral view) ISH for Pax2. Arrows indicate Pax2 mRNA in otic ectoderm in wild-type and no detectable expression in Eya1−/−;Six1−/−. (Scale bars, 50 μm.) (F) Section ISH for Dlx5. (Scale bar, 50 μm.) (G–J) Deletion of Sox2 does not alter Eya1+Six1+ ventromedial (G and H) or Dlx5+ dorsal (I) region in the otocyst but leads to reduction in Neurog1 expression within the neurogenic domain (brackets) of the otocyt (dashed lines). Upper panels in J are dorsal views of whole-mount embryos, and Middle panels are section view. Bottom panels are dark-field images showing sections of the Middle panels coimmunostained with anti-Sox2. A few Sox2+ cells were observed in the dorsal region of the otocyst but not in the neurogenic Neurog1+ domain (brackets). (Scale bars, 50 μm for Bottom and 120 μm for Upper panels.) (K) Lateral view of whole-mount embryos stained for Neurod1 riboprobe. Note the reduction of Neurod1 in V-X ganglia is due to loss of Sox2. (Scale bars, 120 μm.).