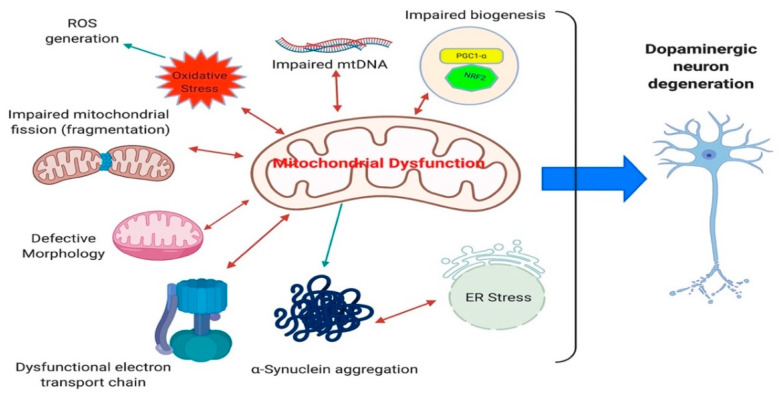
Figure 4.
Pathways of mitochondrial dysfunction, a major cellular and clinical phenotype in PD. Mitochondrial dysfunction can result from impairment in mitochondrial fission, change in mitochondrial morphology, electron transport chain, increase in mtDNA, elevation in oxidative stress leading to reactive oxygen species generation, alteration in mitochondrial biogenesis and electron transport dysfunction. These can lead and associated with protein aggregation and eventual endoplasmic (ER) stress that ultimately results in degeneration of dopaminergic neurons that underlines the PD pathogenesis.