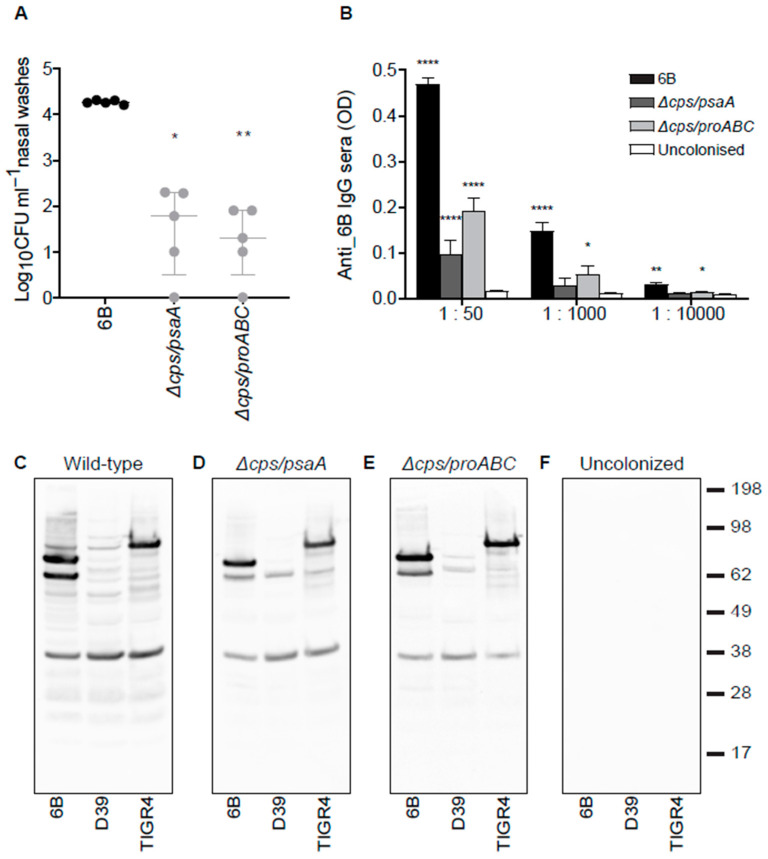
Figure 4.
Wild type 6B and the unencapsulated double mutant strains induce a systemic antibody response after nasopharynx colonisation. (A) Colonisation model; nasal wash CFU 7 days post colonisation of CD1 mice with 1 × 107 CFU of wild type 6B or the double mutant S. pneumoniae strains. (B) Whole-cell enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) anti-6B immunoglobulin (Ig)G responses in mouse sera 28 days post-colonisation with the corresponding strain 6B (black bars), ∆cps/psaA mutant (dark grey bars), ∆cps/proABC mutant (light grey bars) compared with uncolonised controls (white bars). N = 5 for each group and the data analysed using Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s post hoc test to identify significant differences between selected groups; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 ****, p < 0.0001. (C–F) IgG immunoblots for whole-cell lysates of three different S. pneumoniae strains (6B, D39 and TIGR4) probed with sera obtained 28 days after two episodes of colonisation with 6B (C), ∆csp/psaA (D), ∆cps/proABC (E) strains, or from PBS sham colonized mice (F).