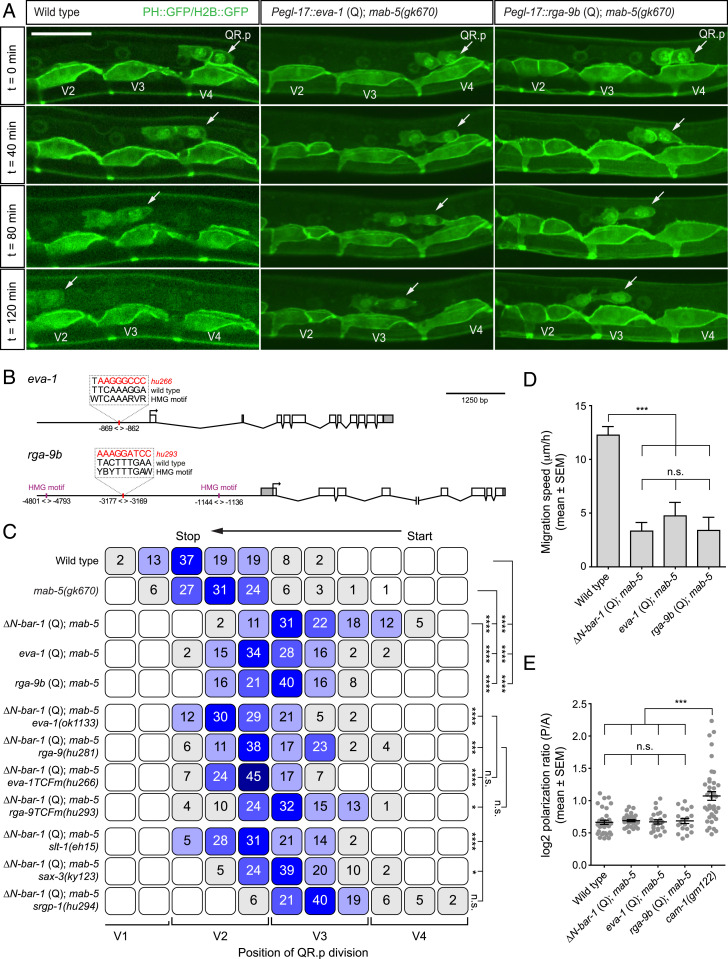
Fig. 5.
eva-1/EVA1C and rga-9b/ARHGAP are required for the canonical Wnt pathway–induced inhibition of QR.p migration. (A) Time-lapse imaging of QR.p migration in wild type and animals specifically expressing eva-1 or rga-9b in the Q neuroblast lineage using the egl-17 promoter. The seam (V) cells and QR.p are marked with nuclear (H2B) and membrane-localized (PH) GFP (huIs63) (38) (scale bar, 15 μm). (B) A schematic representation of the eva-1 and rga-9 loci and the predicted TCF binding sites (HMG motifs) that were mutated. Coordinates are bp from the translational start site of the gene. (C) The position of QR.p division with respect to seam cells, indicated as percentiles of the total number of cells analyzed (n > 50 for all genotypes). The statistical significance was calculated using Fisher’s exact test (n.s., P ≥ 0.05, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001). (D) The average speed of QR.p during the first hour of migration. The bars represent mean ± SEM (n ≥ 50 for all genotypes). The statistical significance was calculated using an unpaired t test (n.s., P ≥ 0.05, ***P < 0.001). (E) Quantification of QR.p polarity as calculated by the ratio of the distance from the nucleus to the posterior and the anterior side of the cell. The black lines indicate mean ± SEM (n ≥ 19 for all genotypes). The statistical significance was calculated using an unpaired t test (n.s., P ≥ 0.05, ***P < 0.001). ΔN-BAR-1 (Q), eva-1 (Q), and rga-9b (Q)–containing strains have mab-5(gk670).