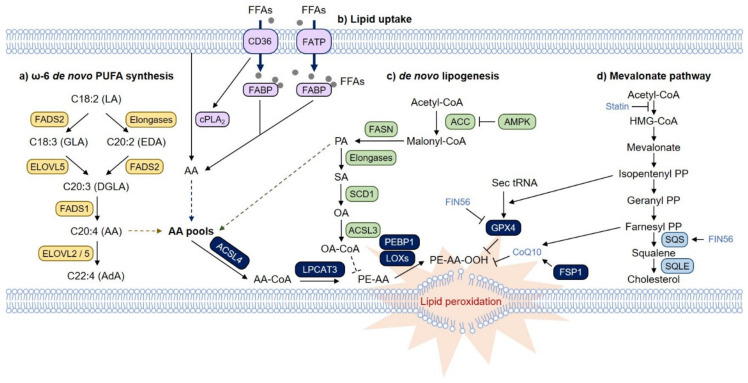
Figure 2.
Lipid metabolic pathways that regulate ferroptosis. (a) In cells, PUFAs can accumulate through the ω-6 de novo PUFA biosynthesis pathway and fatty acid transport pathways via fatty acid translocase (FAT/CD36), fatty acid transport protein (FATP) and fatty acid binding protein (FABP). Imported linoleic acid (LA) is metabolized by elongation of very long-chain fatty acid protein (ELOVL) and fatty acid desaturases (FADS) to synthesize AA and AdA, which are utilized to produce membrane phospholipids. (b) Additionally, AA can be directly imported and transported by FAT/CD36, FATP and FABP proteins. In particular, CD36 activates cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2), releasing AA from phospholipids. The intracellular pools of AA might be the critical checkpoint in ferroptosis and AA-mediated cellular signaling. (c) In contrast, monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA), which is catalyzed from palmitate, a saturated fatty acid (SFA) by stearyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD1), is incorporated into phospholipids in an ACSL3-dependent manner, thereby interfering with the formation of PUFA-phospholipids and protecting cells from ferroptosis. Under glucose deprivation conditions, the depletion of ATPs activate the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway, which suppresses de novo lipogenesis by phosphorylating and inhibiting acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC). As a result, the levels of not only palmitate but also dihomo-γ-linolenic acid (DGLA) and AA are reduced upon glucose starvation, preventing ferroptosis. (d) The mevalonate pathway also provides several critical regulatory axes. Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) is required for the isopentenylation of selenocysteine-tRNA, leading to the synthesis of selenoproteins, including GPX4. Inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase (HMGCR) by statins might induce ferroptosis by inactivating GPX4. FIN56, a class III FIN, degrades GPX4 and activates squalene synthase (SQS). Activation of SQS results in the squalene depletion of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), contributing to ferroptosis. In contrast, inhibition of SQS leads to squalene depletion and facilitates ferroptosis in lymphoma, as squalene also possesses antiferroptotic activity.