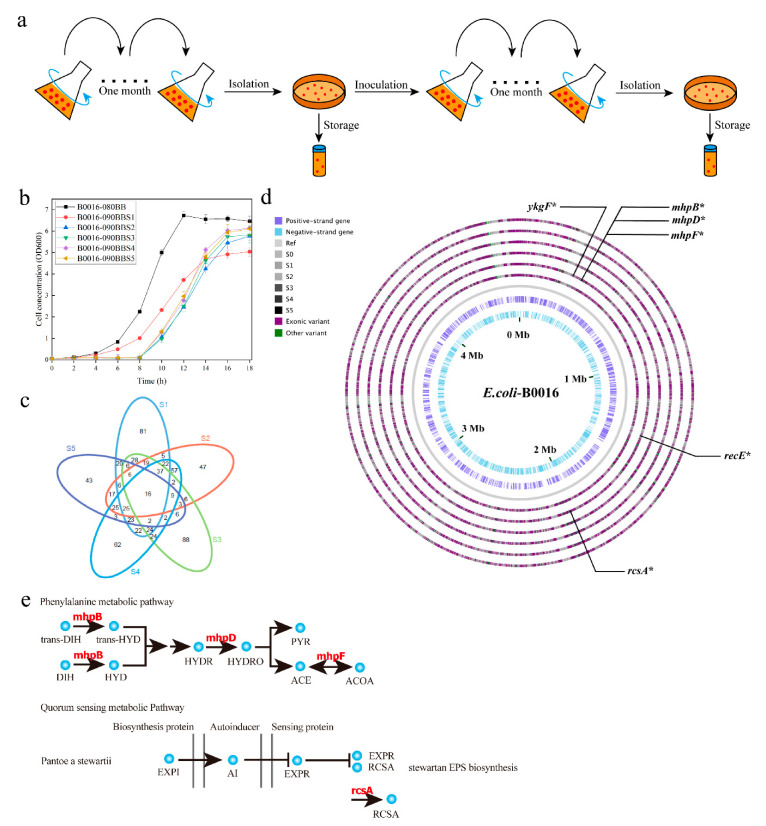
Figure 2.
The method and results of ALE experiment. (a) The process of ALE experiment. (b) The growth curve of the adapted mutants. (c) Consistent mutations among the adapted mutants. (d) Genetic mutations of the mutants. Rings from outer to inner represent the genomic information of B0016-090BBS5, B0016-090BBS4, B0016-090BBS3, B0016-090BBS2, B0016-090BBS1, and B0016-090BB and the reference genome from the NCBI database. S0: B0016-090BB, S1: B0016-090BBS1, S2: B0016-090BBS2, S3: B0016-090BBS3, S4: B0016-090BBS4, S5: B0016-090BBS5. (e) The metabolic pathways associated with the genetic mutation library of the adapted mutant pool. DIH: 2.3-dihydroxycinnamate, HYD: trans- -hydroxy-6-oxononatrienedioate, HYDR: cis-2-hydroxypenta-2,4-dienoate, HYDRO: 4-hydroxy-2-oxopentanoate, PYR: pyruvate, ACE: acetaldehyde, ACOA: acetyl-CoA, EXPI: acyl homoserine lactone, AI: N-(3-oxohexanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone, EXPR: LuxR family transcriptional regulator, quorum-sensing system regulator ExpR, RCSA: LuxR family transcriptional regulator, capsular biosynthesis positive transcription factor.