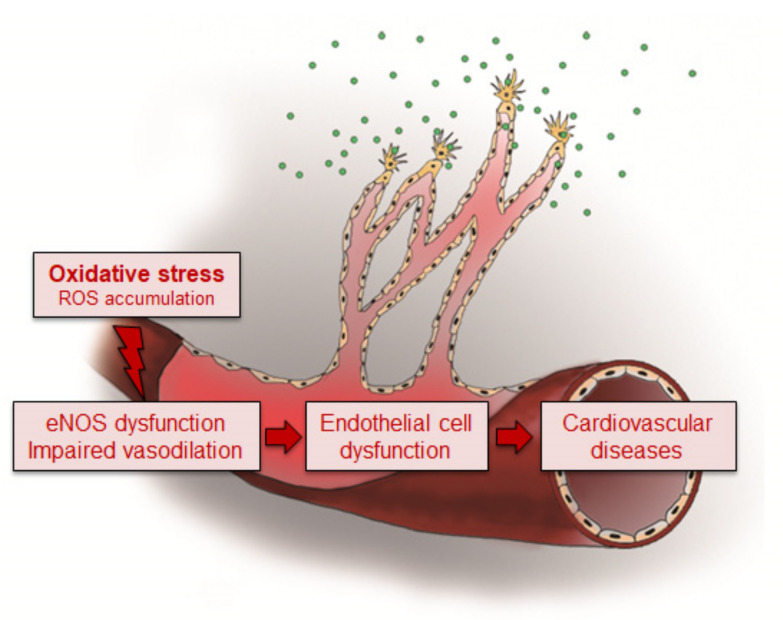
Figure 3.
Oxidative stress induces the progression of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). Oxidative stress plays a central role in the pathogenesis of CVDs. Excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) causes damage to the cellular structure in the vascular wall and induces endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) dysfunction, leading to the impairment of vasodilation by the reduction in nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability. These changes contribute to the structural and functional alteration of the vasculature. The endothelial dysfunction is highly associated with the development of CVDs as an initial step in the process of pathogenesis.