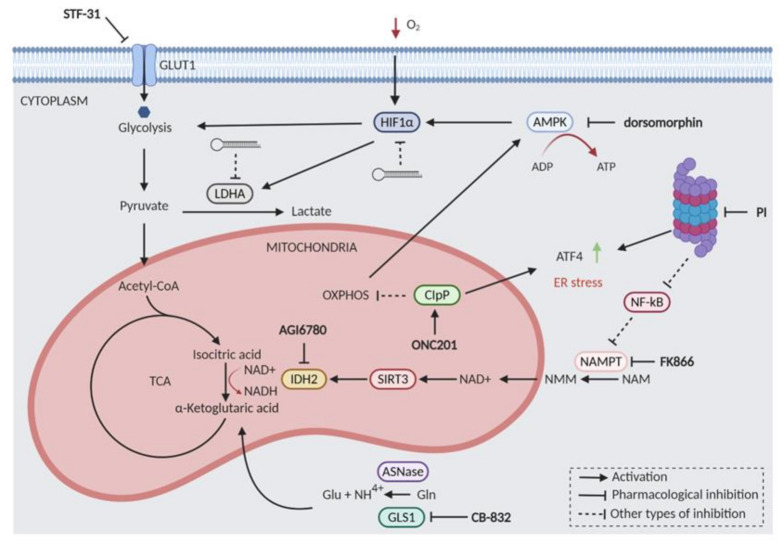
Figure 4.
Proteasome inhibitors and metabolic pathways. Enhancement of glucose and glutamine metabolism is a hallmark of cancer cells, including multiple myeloma (MM). Targeting deranged cellular metabolism at various levels enhances the cytotoxicity of proteasome inhibitors in MM. Inhibition of the glucose transporter GLUT1 (STF-31) or the non-pharmacological inhibition of HIF1α and LDHA enzymes result in synergistic cell death with proteasome inhibitors (PI). The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle enzyme IDH2 is synthetic lethal to PI through NAMPT/SIRT3/IDH2 pathway (AGI-6780, FK866). Degradation of glutamine can be targeted with Asparaginase (ASNase) or Glutaminase inhibitor (CB-832), affecting glutamate-dependent metabolites of TCA cycle. The cellular energy sensor AMPK is synthetically lethal to PI. OXPHOS inhibition by the mitochondrial protease ClpP (ONC201) leads to cellular stress and upregulation of transcriptional factor ATF4.