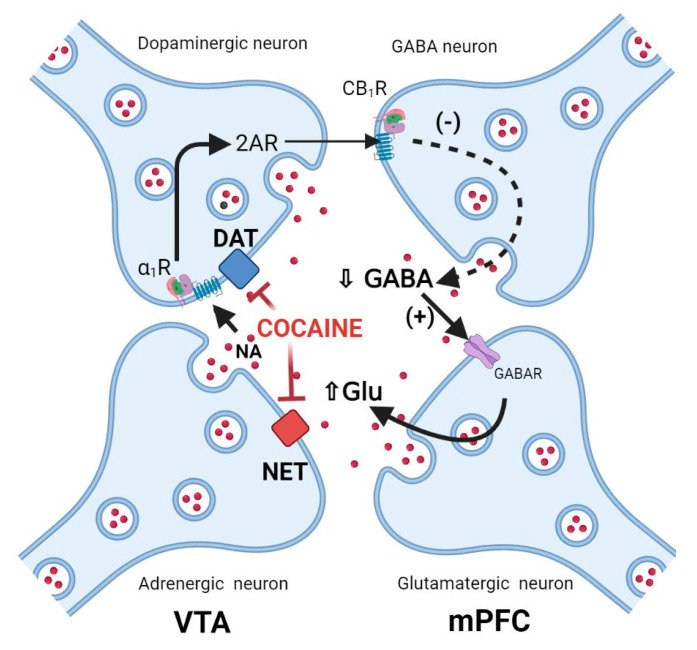
Figure 4.
The proposed mechanism for promoting glutamatergic neurotransmission by cocaine—cocaine inhibits the reuptake of dopamine (DA) and norepinephrine (NA) due to the inhibition of specific dopamine transporter (DAT) and norepinephrine (NET) transporters in medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). NA in the synaptic cleft stimulates α1 (α1R) receptors in DA neurons by promoting the release of endocannabinoids (2-arachidonoylglycerol, 2AR) which, after binding to CB1R receptors, inhibit gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) release in the synaptic cleft. A lower concentration of GABA promotes the release of glutamate (GLU) due to the suppression of the inhibitory effect of GABA on the release of GLU. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 22 January 2021).