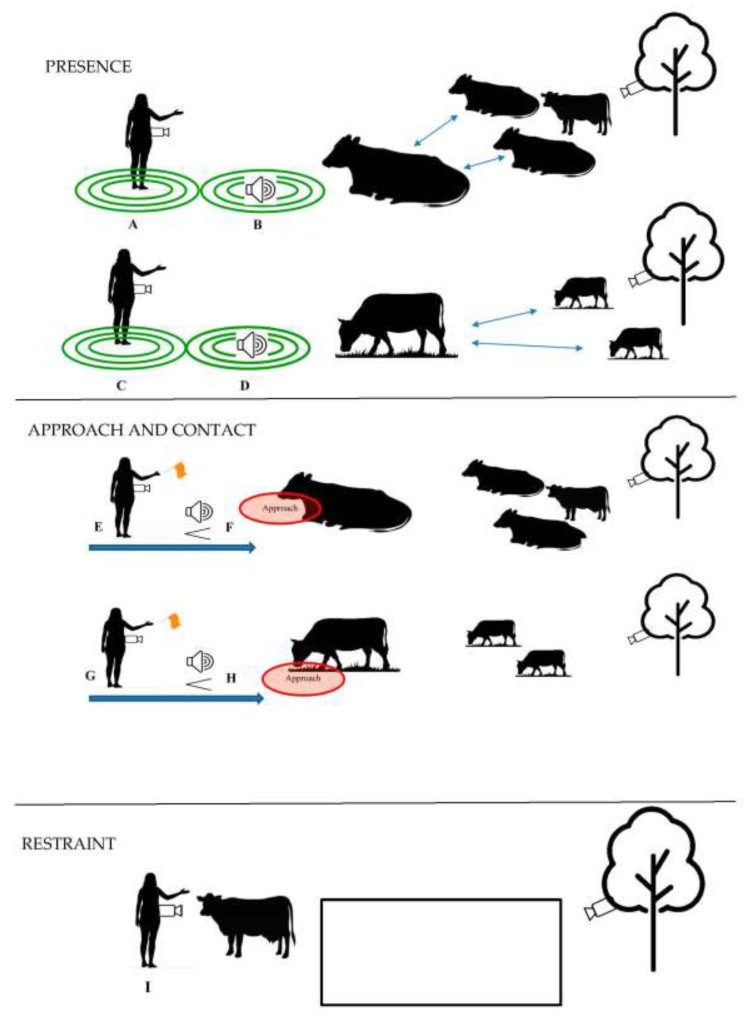
Figure 2.
Schematic of potential HAI experiments to be conducted on-range with beef cows. Tests while cattle are resting (A, B, E & F) can occur near water and shade; tests while cattle are grazing (C, D, G & H) can occur along grazing routes. Resting sites and grazing routes can be determined by preliminary observations of cattle on rangeland. Based on the goals of the experiment, researchers will set a pre-determined distance from which the focal cow is separated from conspecifics depicted by arrows in schematics A–D (e.g., 1 m). Human presence testing is displayed in the top panel. An unfamiliar human (A & C) stands within 10 m of focal cow for 10 min while focal cow is resting or grazing. Hidden speakers (B & D) can be placed at central location where cattle rest or graze, and when focal cow is within 10 m of speaker, unfamiliar human voice can play for 10 min. Green concentric circles indicate proximity zones to measure focal cow’s approach/avoidance distance from human or speaker. Human approach and contact is displayed in the middle panel. An unfamiliar human (E & G) begins 10 m from focal cow and approaches focal cow diagonally from the left side of the focal cow’s head with hand extended and eyes averted at a steady pre-determined pace (e.g., one step per second). If experiment is to capture response to human contact, researcher can pursue physical contact with hand or inanimate, extended object (e.g., flag) in the same standardized manner. Hidden speaker (F & H) can be placed at central location where cattle rest or graze, when focal cow is within 10 m of speaker, unfamiliar human voice plays at ascending volume for 10 s to emulate approaching human. Restraint of cow by human is displayed in the bottom panel. An unfamiliar human (I) begins restraint attempt from 10 m while cow is resting or grazing and attempts to move cow into a square area (2 m × 2 m) marked by spray paint or temporary fencing. Multiple hidden cameras can be fastened onto the unfamiliar human in the test or trees nearby the testing area. Distance from focal cows at beginning of tests (in this example, 10 m) may need to be adjusted based on the herd flight zone sensitivity. Potential behaviors to record include vigilance duration and quality, body/ear position, vocalization quality, approach/avoidance or flight distance based on presence, approach and/or contact, and escape behavior. Limitations of such experiments include characteristics of human, quality of human approach, temporal effects (time, day, season), presence/behavior/identity of adjacent non-focal cows, and cow arousal level.