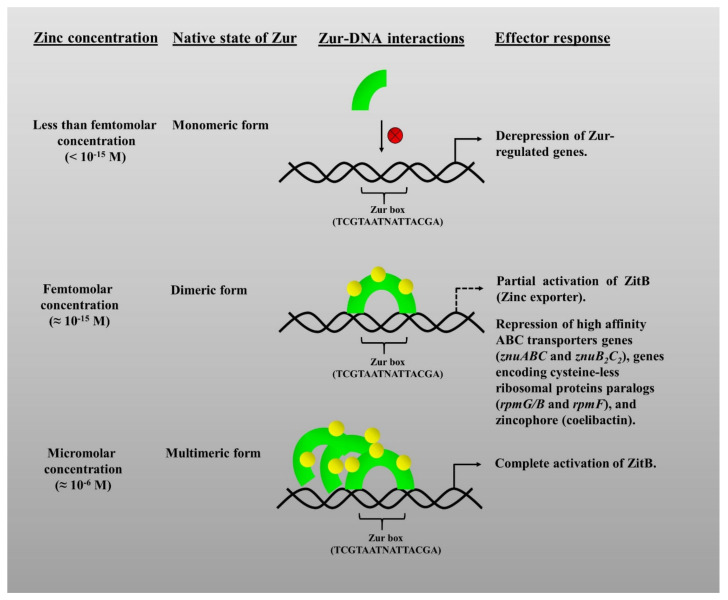
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the graded response of Zur under varying Zn concentrations [62]. The yellow spheres represent Zn metal. Zur loses its DNA-binding affinity at Zur box and causes derepression of its regulon genes when Zn is “less than femtomolar concentrations”. Under femtomolar concentrations of Zn, Zur binds to the DNA and partially activates Zn exporter gene (zitB) and represses the genes for high affinity ABC transporter like znuABC and znuB2C2 and cysteine-rich ribosomal proteins like rpmG/B and rpmF. Under micromolar concentrations, Zur completely activates zitB.