Fig. 1. Anti-NS1 mAb 2B7 is protective against lethal dengue virus infection and NS1-mediated vascular leak and endothelial dysfunction.
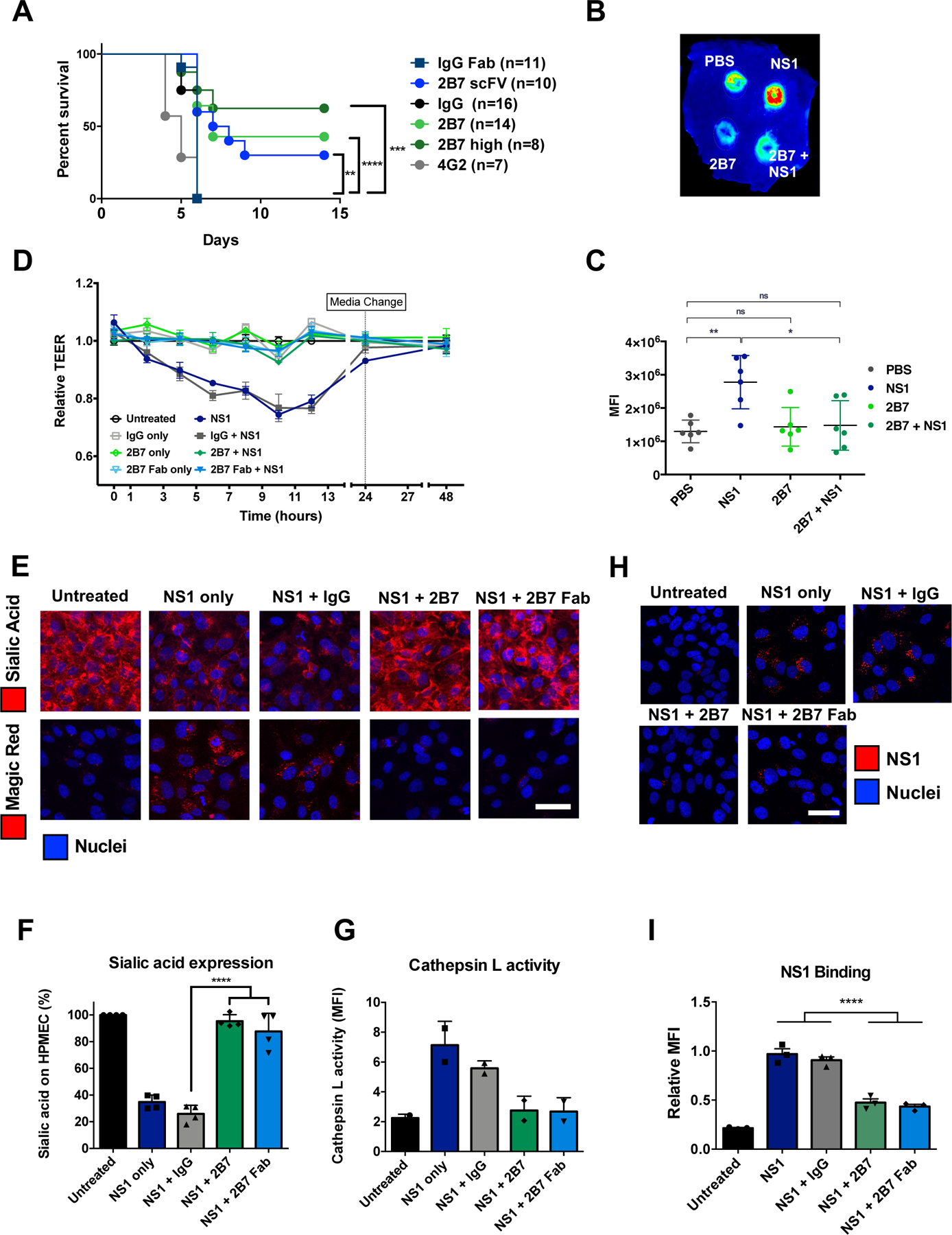
(A) Survival curve of Ifnar−/− mice infected with DENV2-D220. Mice were given two 150-μg doses (300 μg for “2B7 high”) of full-length 2B7, a 2B7 single-chain variable fragment (scFv), an anti-E antibody (4G2), or an isotype control antibody the day before and after infection. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of mice in each group. (B) Localized leak of the tracer molecule, dextran-647, was measured after dorsal intradermal injection of NS1 with or without 2B7, or the indicated controls, into the shaved backs of mice. One representative experiment of n=6 mice is displayed. (C) Quantification of B as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). (D) TEER assay of HPMEC hyperpermeability after addition of DENV2 NS1 with or without 2B7, or the indicated controls, at the indicated time-points post-NS1 treatment. n=3 biological replicates. (E) Endothelial dysfunction and EGL disruption was monitored using immunofluorescent microscopy 6 hours post-treatment of DENV2 NS1 with or without 2B7, 2B7 Fab, or the indicated controls. Endothelial cell dysfunction (bottom, n=2 biological replicates) was monitored using the cathepsin L-activity reporter molecule, Magic Red, and EGL disruption (top, n=4 biological replicates) was monitored by staining sialic acid on the cell surface. (F) and (G) Quantification of E. (H) DENV2 NS1 binding to HPMEC in the presence of 2B7, 2B7 Fab, or the indicated controls, was monitored by immunofluorescent microscopy 90 minutes post-NS1treatment. n=3 biological replicates. (I) Quantification of H. For all figures, scale bars are 50 μm. n.s., not significant p > 0.05; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA analysis with multiple comparisons.
