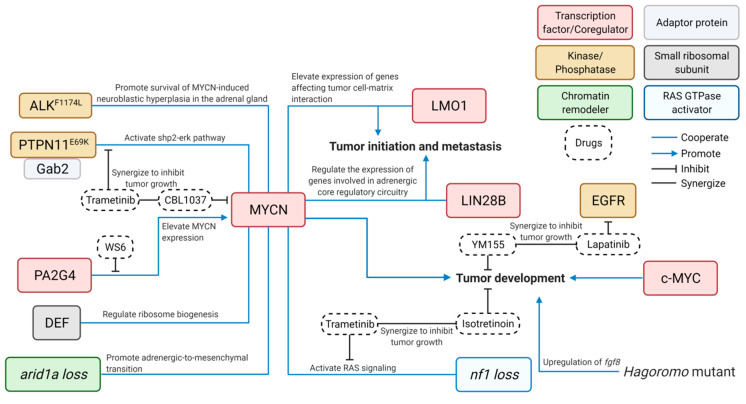
Figure 2.
Cooperative contributions of diverse signaling pathways to the pathogenesis of NB—findings from zebrafish models. Blue lines connect cooperative genes in NB pathogenesis; Blue arrows indicate positive impact; Bar-headed lines indicate inhibitory effect; and Black lines indicate synergy between drugs. ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase; arid1a, AT-rich interacting domain–containing protein 1A; c-MYC, V-Myc avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog; DEF, digestive organ expansion factor; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; Gab2, GRB2-associated-binding protein 2; LIN28B, lin-28 homolog B; LMO1, LIM domain only 1; MYCN, V-Myc avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene neuroblastoma; nf1, neurofibromatosis type 1; PAG2G4, proliferation-associated protein 2G4; and PTPN11, protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 11. This figure was created with BioRender.com.