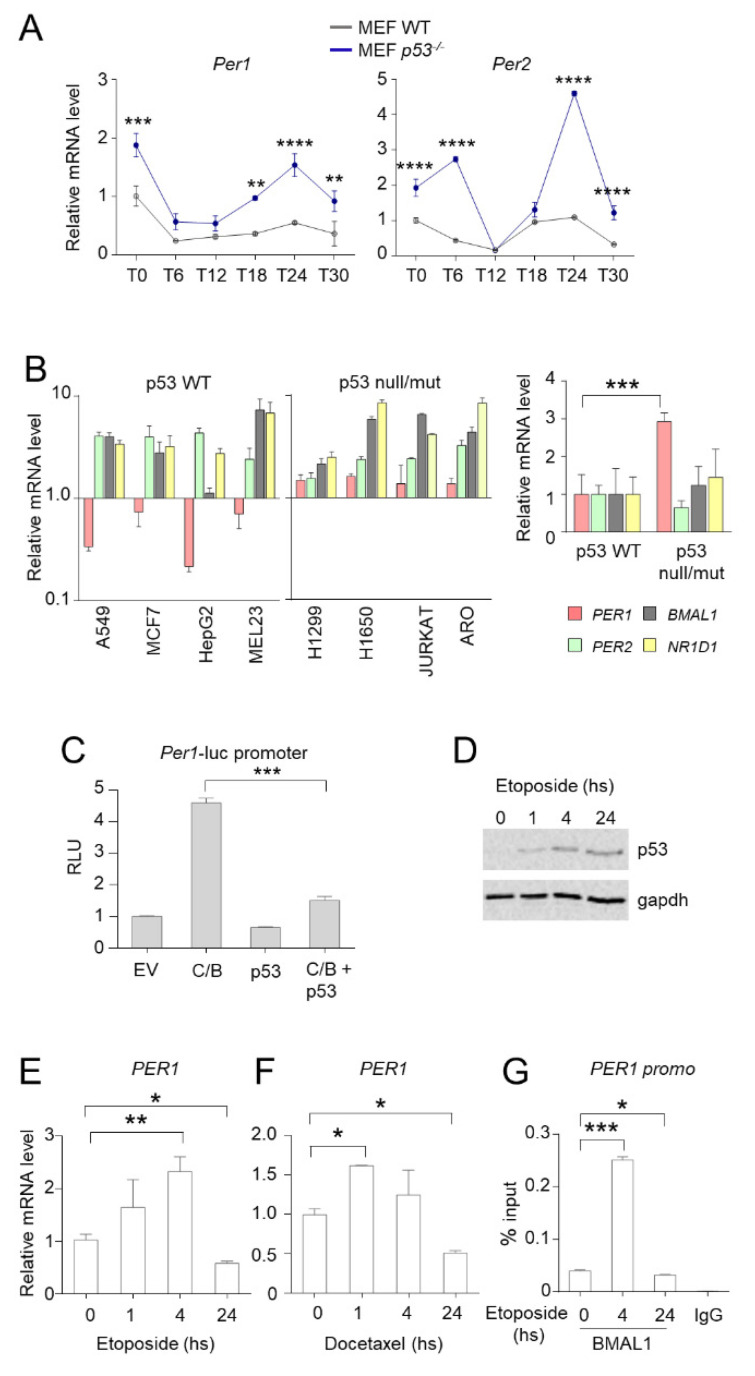
Figure 3.
Control of PER1 expression by p53. (A) Circadian expression of Per1 and Per2 in MEFs WT and p53−/−. Real-time PCR analysis was performed from RNAs prepared at the indicated times after serum shock synchronization. T0, unsynchronized cells. Bars represent average ± SD (n = 2). (**) p < 0.01, (***) p < 0.001, (****) p < 0.0001. (B) Q-PCR analysis of PER1, PER2, BMAL1 and NR1D1 from RNA samples prepared from different human cancer cell lines. Espression value in non-tumoral HEK-293 cells was set to 1. Bars represent average ± SD (n = 3). Right, average levels of expression of the same genes in p53 wild-type cell lines (A549, MCF7, HepG2, MEL23) versus p53 null/mut cell lines (H1299, H1650, JURKAT, ARO). Bars represent average ± SD. (***) p < 0.001. (C) Evaluation of the activation of Per1 promoter by luciferase assay in HEK-293 cells transfected with the indicated plasmids (C/B = Clock/Bmal1; ev = empty vector). Levels of expression are relative to the control transfected with empty vector, after normalization for transfection efficiency through beta-galattosidase assay. Bars represent average of RLU (relative luciferase units) ± SD (n = 3). (***) p < 0.001. (D) Expression of p53 following treatment with etoposide for the indicated time in A549 cells, evaluated by WB. Gapdh was used as loading control. (E–F) PER1 mRNA expression levels in A549 cells treated with etoposide (E) or docetaxel (F) for the indicated time. Bars represent average ± SD (n = 2). (*) p < 0.05, (**) p < 0.01. (G) ChIP from A549 cells treated with etoposide for the indicated time. Cells were collected after treatment, subjected to dual cross-link and ChIP with BMAL1 antibody or mouse IgG was performed. Primers for PER1 promoter were used for qPCR. BMAL1 enrichment was shown as % of input. Bars represent average ± SD (n = 3). (*) p < 0.05, (***) p < 0.001.