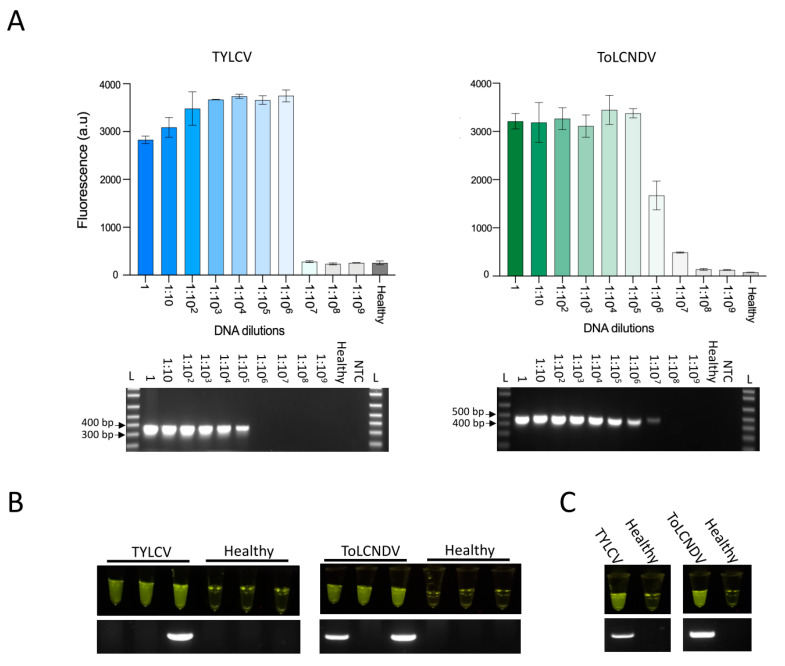
Figure 2.
Detection of TYLCV and ToLCNDV in infected plants. (A) Comparison of Cas12-based detection (top) and conventional PCR detection (bottom) of 10 serial dilutions of TYLCV and ToLCNDV DNA from infected Nicotiana benthamiana plants. Different dilutions of DNA extracted from plants infected with TYLCV (left) or ToLCNDV (right) or noninfected plants (healthy) were used as input for the LAMP reactions at 65 °C for 40 min as well as PCR. LAMP products were subsequently added to the Cas12a detection reactions. The Cas12a detection assay was performed at 37 °C, and collateral activity was measured by HEX reporter fluorescence after 30 min. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). Conventional PCR products were resolved on a 1% agarose gel. L: 1 kb plus ladder (Invitrogen). (B) Comparison of Cas12a-based virus detection with visual in-tube fluorescence readouts (top) and conventional PCR (bottom) of three independent N. benthamiana plants infected with TYLCV (left panel) or ToLCNDV (right panel) or noninfected plants (healthy). (C) Comparison of Cas12a-based virus detection with visual in-tube fluorescence readouts (top) and conventional PCR (bottom) of tomato plants infected with TYLCV (left panel) or ToLCNDV (right panel) or noninfected plants (healthy).