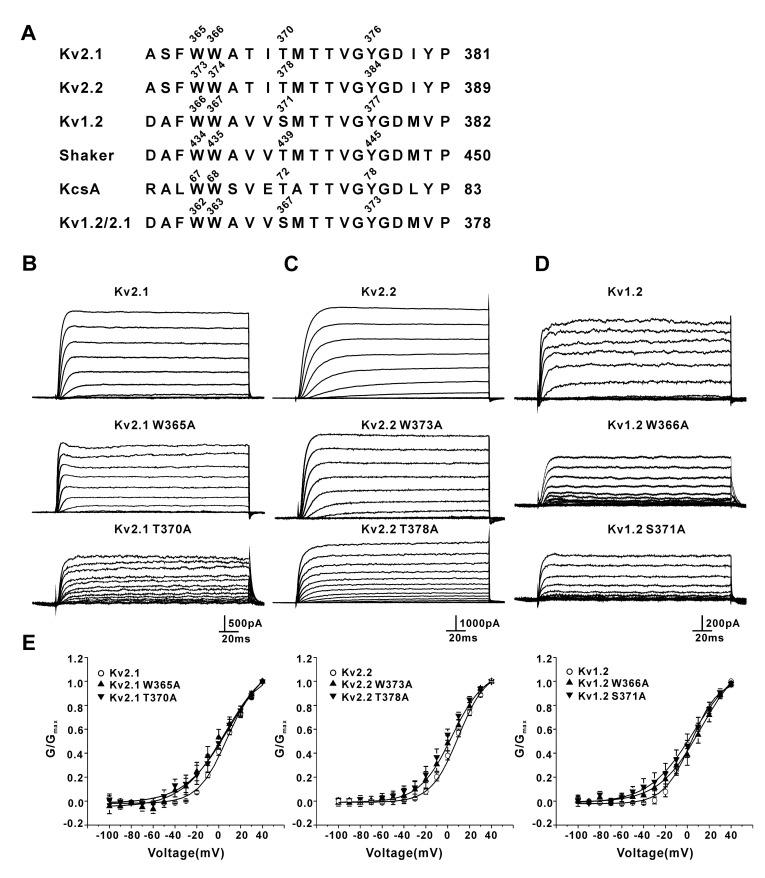
Figure 1.
Effects of the mutation of the equivalent residues controlling the slow inactivation of Shaker channels on the rat Kv2.1, Kv2.2, and Kv1.2 channels. (A) Sequence alignment of the selectivity filter and pore helix of various K+ channels: Kv2.1 (GI: 6981120), Kv2.2 (GI: 164663795), Kv1.2 (GI: 25742772), Shaker (GI: 288442), KcsA (GI: 61226909), and the Kv1.2/Kv2.1 chimeric channel (PDB: 2R9R). (B) Representative currents for the Kv2.1 wild-type, W365A, and T370A mutant channels (−100 to +40 mV, 200 ms, in 10-mV increments; n = 8~14). (C) Representative currents for the Kv2.2 wild-type, W373A, and T378A mutant channels (n = 7~12). (D) Representative currents for the Kv1.2 wild-type, W366A, and S371A mutant channels (n = 6–9). (E) G-V curves of the wild-type and mutant Kv channels.