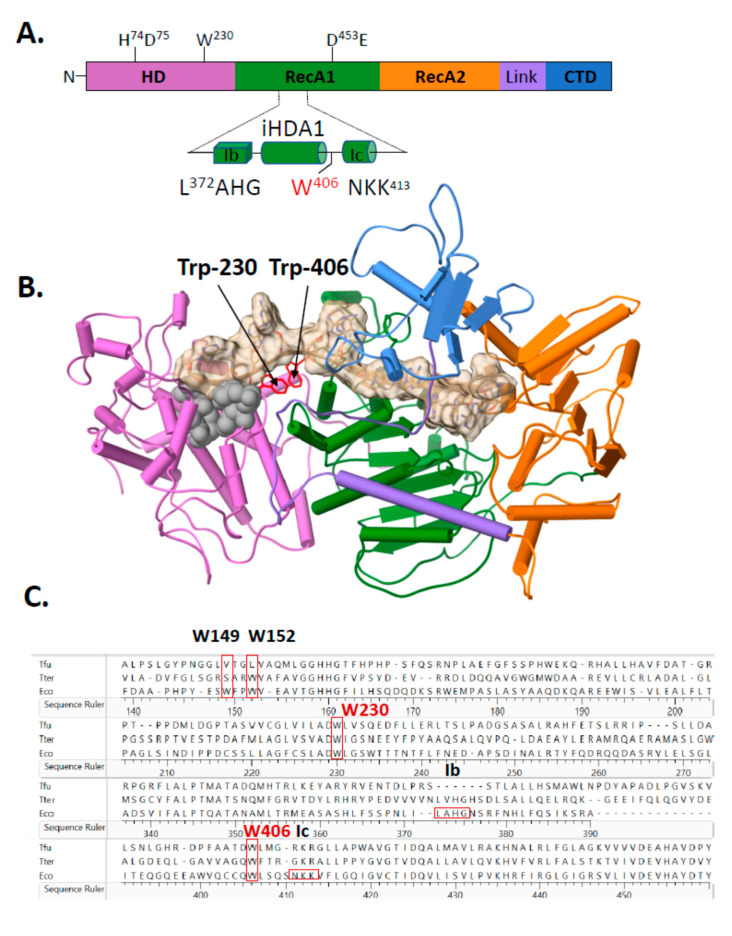
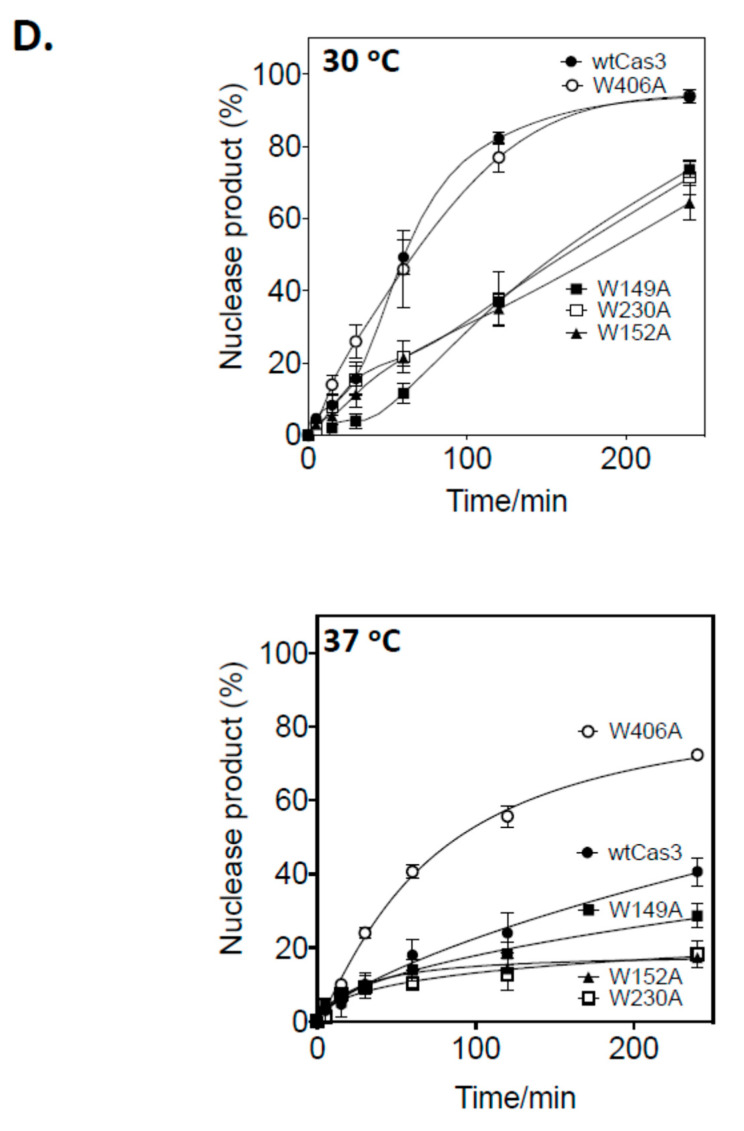
Figure 2.
Structural positioning of two invariant tryptophan residues at the interface of Cas3 HD and RecA1 domains—a key role in Cas3 nuclease function for Trp-406. (A) Cartoon representation of Cas3 protein with amino acid residues indicated for the nuclease (HD) and Walker B ATPase active sites using numbering from the E. coli protein. Highlighted in the foreground is the region detailed in the results, located at the interface of HD and RecA1 domains (‘iHDA1’) and including the ssDNA binding helicase motifs Ib and Ic. (B) E. coli Cas3 structure deduced from T. fusca Cas3 (PDB: 4QQW) and T. terrenum (PDB: 4Q2C) (27,35) highlighting the tryptophan residue W406 (labelled) and the passage of ssDNA (tan cord). Cas3 regions are denoted as follows in the same way as in part A: HD (orchid), RecA1 (green), RecA2 (orange), an interdomain linker helix (purple) and the CTD (blue). Grey spheres indicate the HD nuclease active site residues. (C) Sequence alignment highlighting conservation of residues Trp-406 and Trp-230 in Escherichia coli K-12 (Eco) with the structurally determined Cas3 proteins from T. fusca (Tfu) and T. terrenum (Tter) proteins. Protein sequences were aligned using Clustal Omega and results were exported via Lasergene 17. (D) Nuclease activity of Cas3 and mutants (56 nM) measured on the DNA fork substrate (20 nM). Samples were collected at 0, 5, 15, 30, 60, 120 and 240 min. Reactions were carried out in triplicate at 30 °C or 37 °C as indicated, and data points show standard errors from the mean.