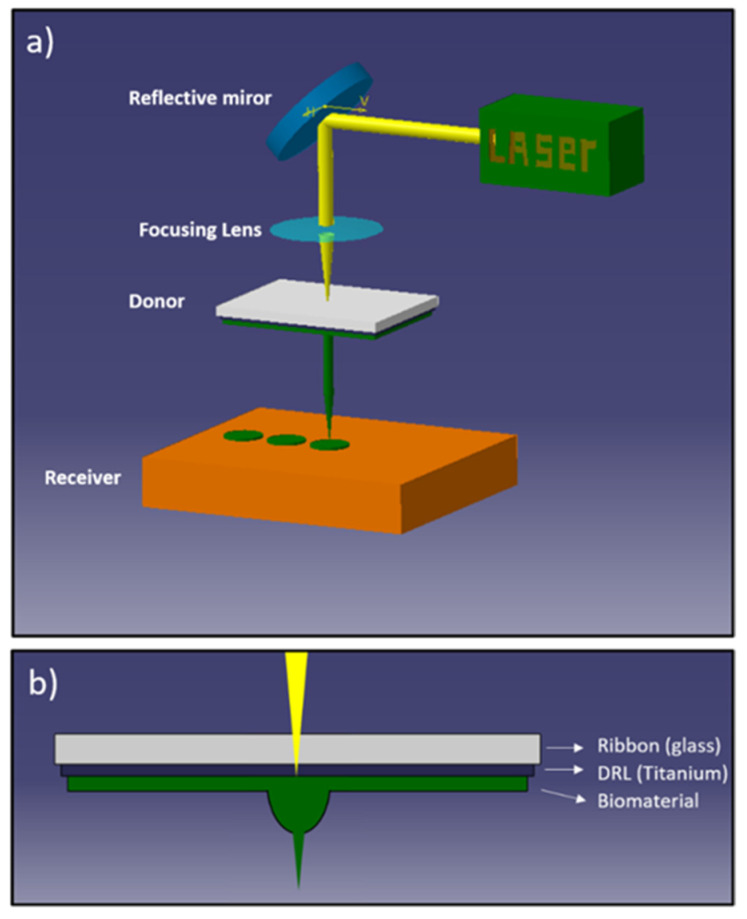
Figure 9.
(a) Sketch of laser-assisted bioprinting technique: the laser pulse is focused by a lens on the donor substrate surface. The laser–matter interaction induces the ejection of the targeted material and its deposition on the receiver substrate in close proximity. (b) Zoom on the donor substrate during biomaterial ejection: the laser–matter interaction with the absorbing dynamic release layer (labelled DRL) creates an expanding and highly confined plasma, which leads to the generation of a hemispherical cavitation bubble which pushes the biomaterial layer away from the donor substrate [157].