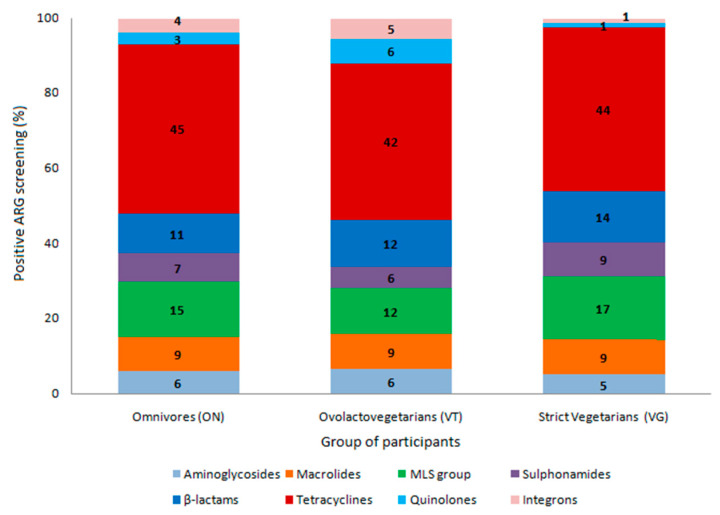
Figure 1.
Frequency of detection of antimicrobial resistance genetic markers (ARG) related to different classes of antimicrobial drugs according to positive screening by PCR from the fecal metagenome of omnivores (ON), ovolactovegetarians (VT), and strict vegetarians (VG). ARG are clustered based on their chemical structure or phenotype, such as β-lactams (blaCTX-M, blaTEM, blaSHV, blaZ, mef); tetracyclines (tet(A), tet(B), tet(E), tet(L), tet(M), tet(O), tet(Q)); macrolide, lincosamide, and streptogramin (MLS) group (ermA, ermB, ermC); quinolones (qnrB, qnrS); sulfonamides (sul1, sul2); aminoglycosides (aacA-aphD); and integrons (intl-1, intl-2).