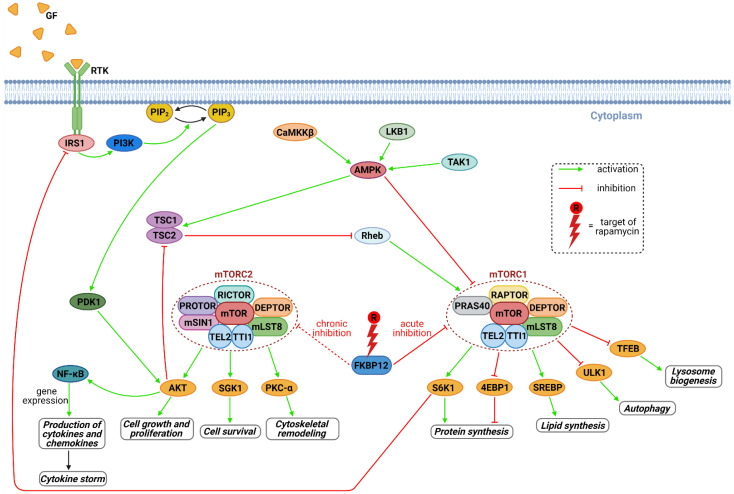
Figure 4.
The mTOR signaling pathway and its important regulatory functions are shown. Activated mTORC1 results in increased protein synthesis via downstream effectors S6K1 and 4EBP1. AKT-mediated activation of NF-κB increases gene expression followed by cytokine and chemokine production. Rapamycin acts as the inhibitor of mTORC1 (acute inhibition) and mTORC2 (chronic inhibition) that is crucial for affecting of the downstream pathway. Abbreviations: 4EBP1, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1; AKT, protein kinase B; AMPK, 5’-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; CaMKKβ, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-β; DEPTOR, DEP domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein; FKBP12, FK506-binding protein of 12 kDa; GF, growth factors; IRS1, insulin receptor substrate 1; LKB1, liver kinase B1; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; mLST8, mammalian lethal with SEC13 protein 8; mSIN1, mammalian SAPK interacting protein 1; PDK1, 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate; PKC-α, protein kinase C alpha; PRAS40, proline-rich AKT substrate of 40 kDa; PROTOR, protein observed with rictor; RAPTOR, regulatory associated protein of mTOR; Rheb, ras homolog enriched in brain; RICTOR, rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; S6K1, ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1; SGK1, serum- and glucocorticoid-induced kinase 1; SREBP, sterol regulatory element binding protein 1; TAK1, TGF-β activated kinase 1; TEL2, telomere maintenance 2; TFEB, transcription factor EB; TSC1 and 2, tuberous sclerosis complex 1 and 2; TTI1, TEL2-interacting protein 1; ULK1, Unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase. Figure was created with BioRender.com.