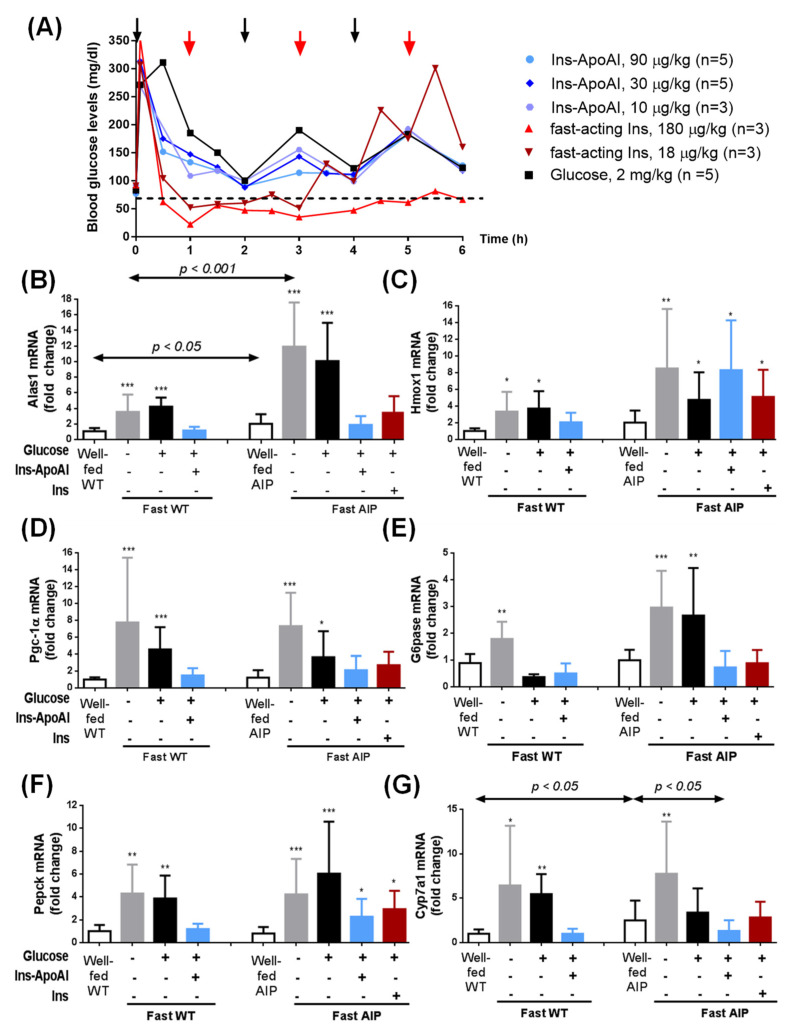
Figure 2.
Transcriptional analysis of important genes in fasted animals treated with glucose, and glucose with a fast-acting insulin or an experimental liver-targeted insulin (Ins-ApoAI). (A) Serum glucose kinetics over 6 h measured after glucose overloads in 15-h-fasted AIP mice treated with glucose. Glycemia was measured at 30 min intervals, starting 5 min post-initial dose. Black arrows represent glucose administration for all groups and red arrows represent supplementary glucose administration for the fast-acting insulin group. Kinetics of the (B) alas1, (C) hmox1, (D) pgc-1α, (E) g6pase, (F) pepck, and (G) cyp1a7 gene transcription in the liver were measured in male WT and AIP mice at baseline (well-fed condition), 15-h-post starvation and after the administration of three doses of glucose (2 mg/kg, i.p.), three doses of glucose with a single subcutaneous dose of Ins-ApoAI (eq. from 90 µg/kg of crystallized insulin equivalent) or six doses of glucose with a single dose of a commercial fast-acting insulin (10 ui/mL, eq. to 18 µg/kg). Data are mean ± s.d. of five animals per group. Comparisons were performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc correction. Alas1, aminolevulinate synthase 1; hmox1, heme oxygenase-1; pgc-1α, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1 alpha; g6pase, glucose 6-phosphatase; pepck, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and cyp1a7, cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 vs. well-fed mice and. Ins-ApoAI, the fusion protein of a single chain insulin and apolipoprotein A-I.