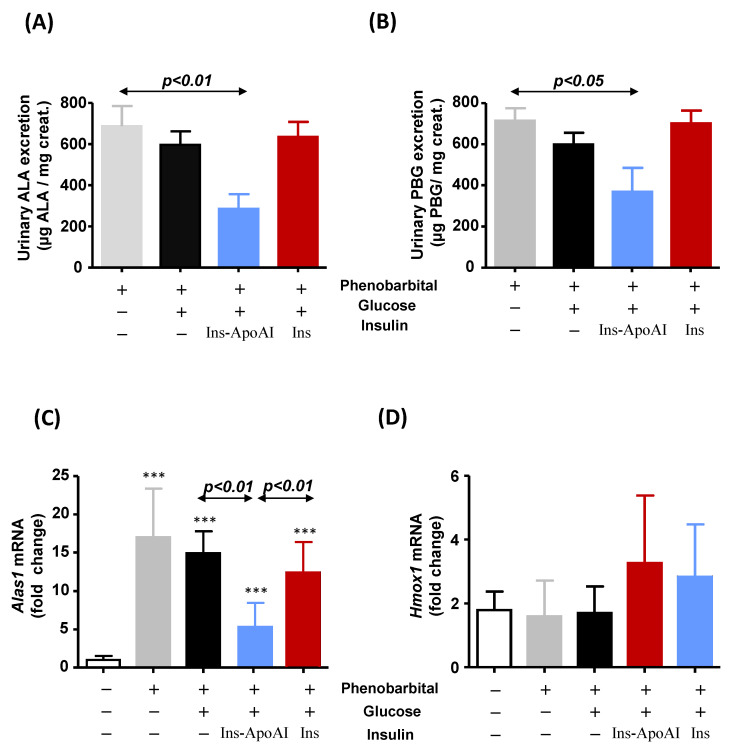
Figure 3.
Therapeutic efficacy of subcutaneous administration of Ins-ApoAI and glucose during an ongoing phenobarbital-induced attack. Urinary (A) ALA and (B) PBG excretion on day 4 of the phenobarbital-induced attack. While co-administration of glucose and Ins-ApoAI halved the excretion, glucose alone or glucose co-administered with fast acting insulin failed to reduce the excretion of the neurotoxic precursors ALA and PBG. Hepatic expression of (C) alas1 and (D) hmox1 measured on day 5, 20 min after a supplementary phenobarbital dose of 90 mg/kg. Data are mean ± s.d. of at least four animals per group. Comparisons were performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test. ***, p < 0.001 vs. control untreated AIP mice. Daily urinary excretion of porphyrin precursors corresponding to baseline values are: 52 ± 12.7 µg ALA/mg creat. and 11.8 ± 4.2 µg PBG/mg creat. Alas1, aminolevulinate synthase 1; hmox1, heme oxygenase-1. Ins-ApoAI, the fusion protein of a single chain insulin and apolipoprotein A-I.