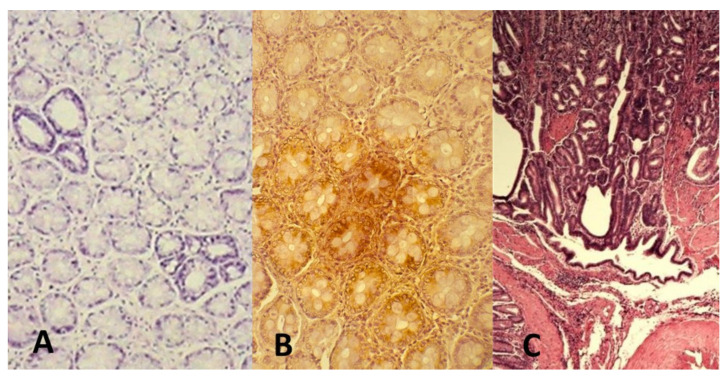
Figure 1.
AOM-induced CRC in rat. AOM is an azide compound, active derivative of DMH and induces genetic damage in the colon cells. The carcinogen promotes classical colon carcinogenesis events with adenomas to carcinoma progression [56]. (A) aberrant crypts with (B) overexpression of p21 k-ras protein (dark brown) and (C) development of infiltrating adenocarcinoma after 32 weeks from the induction (original microphotographs from Luca Vannucci’s Lab archive).